Eczema Nummularis
What is eczema nummularis?
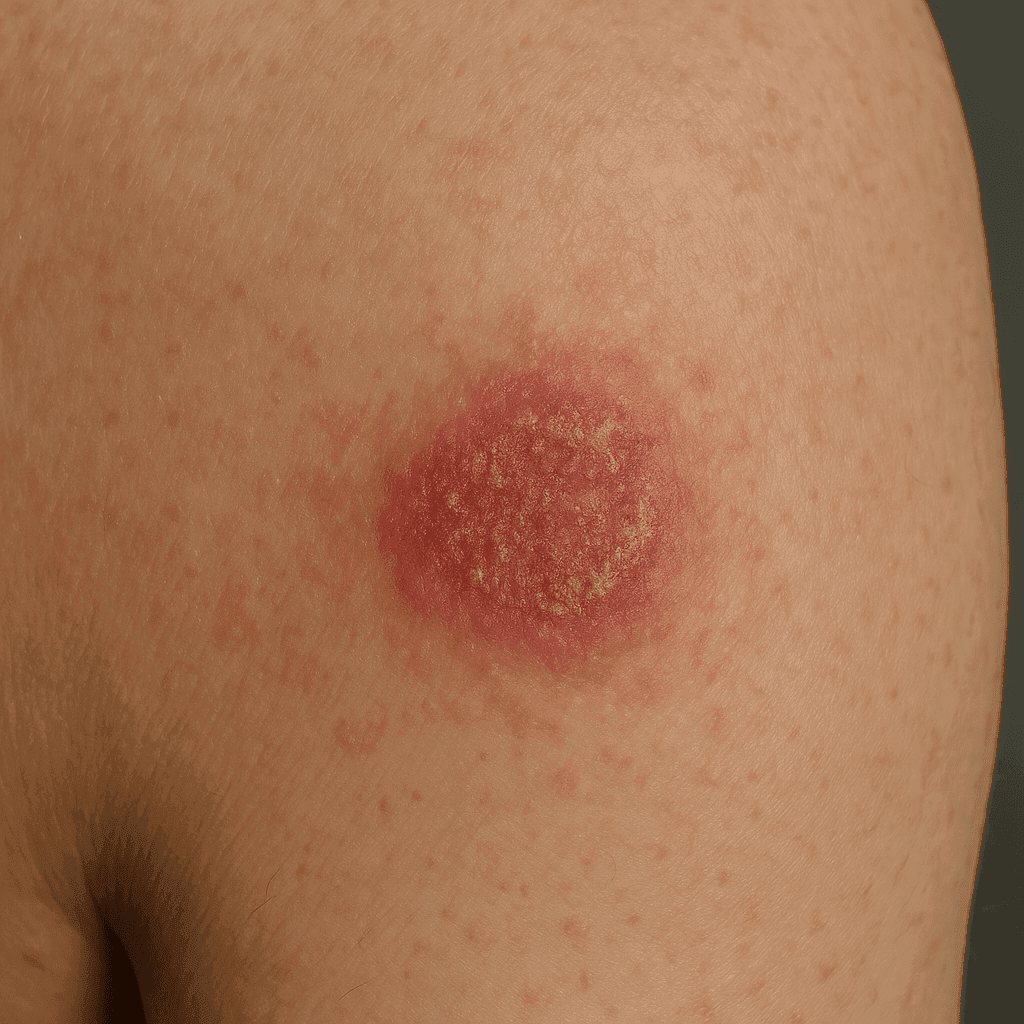
Frothy eczema, also known as eczema nummularis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by round, itchy patches. These skin lesions can resemble coins, hence their name. This eczema is often confused with other skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis.
What does frothy eczema look like?
The skin lesions are usually well-demarcated, red or brownish, and may be covered with scales. They can appear on different parts of the body, but are most common on the extremities. Itching is one of the main symptoms, often leading to scratching, which can worsen the skin condition.
Symptoms of frothy eczema
Symptoms of frothy eczema can vary from person to person, but most commonly include itching, redness and dry skin. In adults, these lesions can be more pronounced and persistent, often leading to discomfort in daily life.
Typical symptoms in children
In children, frothy eczema may take a milder form, but it should not be taken lightly. Skin lesions in children may be less extensive, but itching can lead to sleepless nights and irritability. It is important to properly moisturize your child's skin and avoid irritants.
Causes and risk factors
Although the exact causes of frothy eczema are not fully understood, there are several factors that can increase the risk of this disease.
Genetic factors
As with many skin diseases, genetics plays a significant role. Individuals with a family history of atopic dermatitis, asthma or allergies are more likely to develop foamy eczema.
Impact of environment and allergies
Environmental factors such as cold weather, low humidity and contact with irritating chemicals can exacerbate symptoms. Allergies to foods, pollen or animal dander can also affect the development and severity of the disease.
The role of stress in the development of the disease
Stress is an often underestimated factor in skin health. In the case of frothy eczema, stress can exacerbate symptoms and cause relapses. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can be helpful in managing symptoms.
Diagnosing frothy eczema
Diagnosing foamy eczema is based on a thorough clinical evaluation. Dermatologists usually diagnose the disease based on its characteristic symptoms, but in some cases additional skin tests may be necessary.
Diagnostic methods
Allergy tests, skin biopsies and evaluation of the patient's history can help differentiate freckled eczema from other skin conditions.
Treatment of frothy eczema
Treatment of frothy eczema includes both pharmacotherapy and topical therapies. The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Pharmacotherapy
Corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation. Antihistamines can be used to relieve itching, which helps prevent scratching and worsening of the skin condition.
Topical therapies
The use of moisturizing creams and ointments is key to keeping the skin hydrated. Medicated baths with oils or salves can also provide relief from symptoms.
Home and natural treatments
Some people choose to use herbs and supplements to support treatment. Calendula, aloe vera or tea tree oil extracts are popular. Dietary changes, such as avoiding allergenic foods, can also help control symptoms.
Foley eczema and lifestyle
Lifestyle has a significant impact on the course of the disease.
Importance of diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins can promote skin health.
Avoiding irritants
Avoiding contact with irritants and tobacco smoke is key to preventing recurrence.
Stress management techniques
Regular exercise, meditation and other relaxation techniques can help reduce stress, which is often a factor in exacerbating symptoms.
Prevention of frothy eczema
Preventing the recurrence of foamy eczema requires regularity and diligence in skin care.
How to prevent recurrences?
Regular use of moisturizers and avoidance of irritants is key. Proper hygiene and avoiding prolonged contact with high-temperature water are also worthwhile.
Foam eczema vs. other skin diseases
Comparison with atopic dermatitis
Foam eczema and atopic dermatitis share many symptoms, but differ in the course and location of the lesions. Atopic dermatitis is more related to genetics and often occurs from early childhood.
When to consult a doctor?
It is a good idea to consult a doctor if the symptoms of frothy eczema do not subside despite the use of home treatments. Preparing for the visit includes gathering information about medications used and observations about the condition of the skin.
Summary
Frothy eczema is a chronic skin condition that can affect quality of life. Early recognition and appropriate treatment are key to minimize discomfort and prevent recurrence. Systematic care, avoidance of irritants and a healthy lifestyle can greatly improve symptom control.
Frequently asked questions
FAQs about eczema frothyhead.
Is frothy eczema contagious?
No, foamy eczema is not a contagious disease.
What are the most common triggers for symptoms?
Triggers include stress, allergens and weather changes.