Photodermatoses: Skin Reactions to Sunlight
Understanding sun-induced skin reactions and treatments.
Introduction
Photodermatoses refer to a group of skin conditions that are triggered or exacerbated by exposure to sunlight. These reactions can vary significantly in severity and presentation, often leading to discomfort and impacting the quality of life for affected individuals. Understanding these conditions is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Sun-induced skin reactions are more common than many realize, and they can sometimes be mistaken for other dermatological issues. As such, raising awareness about photodermatoses is important for early recognition and management. With the right knowledge, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin and reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
What are Photodermatoses?
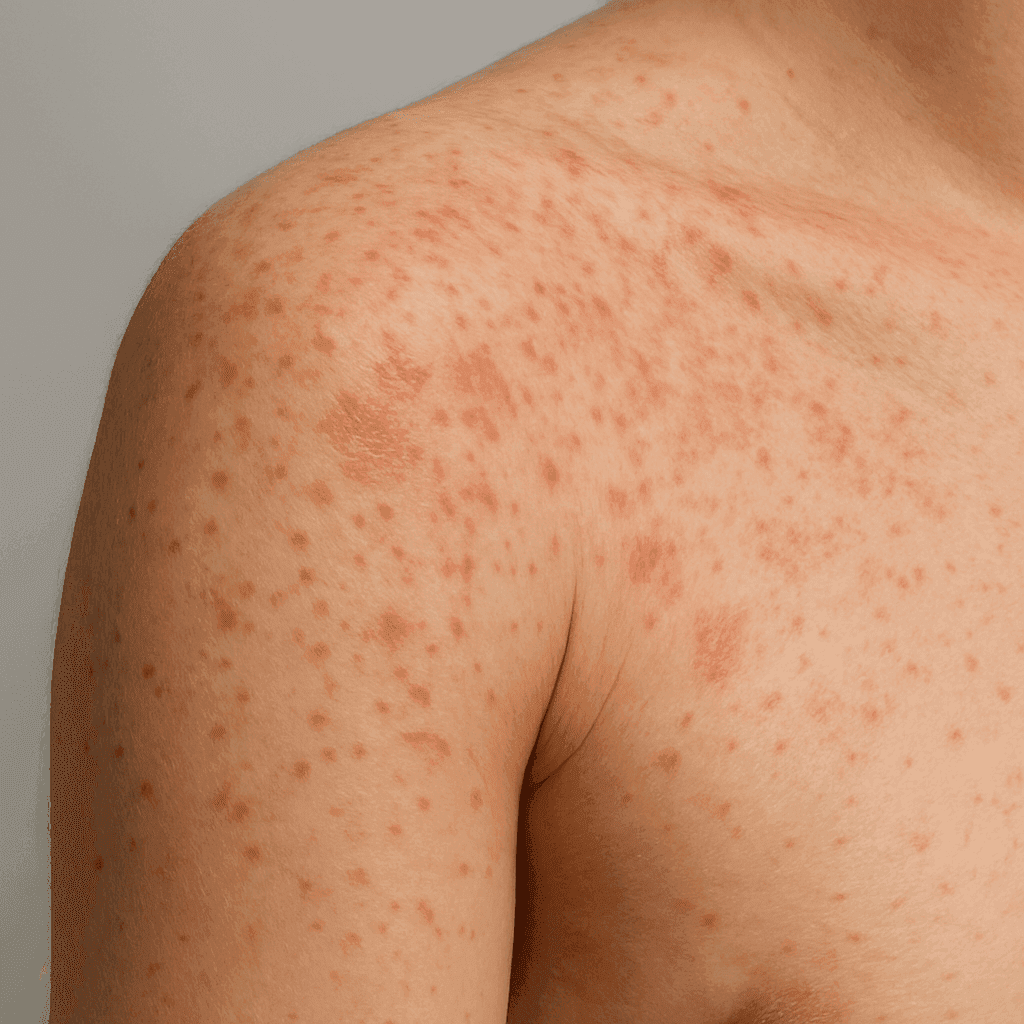
Photodermatoses are defined as skin disorders that are induced or aggravated by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. These conditions are characterized by abnormal skin reactions to sunlight, which can include rashes, blisters, or other forms of irritation.
Common Types of Photodermatoses
Several types of photodermatoses exist, each with its own distinct features. Some of the most common include:
- Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE): A common reaction characterized by itchy red rashes.
- Solar Urticaria: A condition where hives develop quickly after sun exposure.
- Chronic Actinic Dermatitis: A severe, chronic form of photodermatoses that involves persistent eczema-like symptoms.
These conditions can affect individuals differently, and understanding their nuances is critical for effective care.
Causes of Photodermatoses
The causes of photodermatoses can be multifaceted, often involving a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as individuals with certain genetic markers are more susceptible to these conditions.
Environmental Triggers and UV Radiation
Environmental factors, particularly UV radiation, are primary triggers for photodermatoses. UV rays can alter skin cells and provoke immune responses, leading to inflammation and the characteristic symptoms associated with these conditions. External elements such as certain medications and topical products can also sensitize the skin, increasing susceptibility to sunlight.
Understanding these causes can help individuals identify personal risk factors and implement effective preventive measures.
Symptoms of Sun-Induced Skin Reactions
The symptoms of photodermatoses can vary widely, depending on the specific type and individual response. Common symptoms include redness, itching, blistering, and in severe cases, pain or burning sensations on affected areas. These symptoms typically appear shortly after sun exposure, making timely recognition crucial.
Differentiating Between Types
Identifying the specific type of photodermatosis is essential for appropriate management. For instance, PMLE usually presents with small red bumps or blisters, while solar urticaria manifests as hives that develop rapidly after sun exposure. By distinguishing these symptoms, individuals can seek targeted treatments and advice from healthcare professionals.
Diagnosing Photodermatoses
Diagnosis of photodermatoses typically involves a comprehensive clinical evaluation by a dermatologist. This assessment may include a detailed medical history and a physical examination of the affected skin.
Diagnostic Tests and Dermatologist Role
In some cases, additional diagnostic tests such as phototesting or photopatch testing may be required to confirm the diagnosis and ascertain the specific type of photodermatosis. Dermatologists play a vital role in this process, utilizing their expertise to differentiate between similar conditions and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Photodermatoses
There are several treatment options available for managing photodermatoses, ranging from topical applications to more advanced therapies. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and type of the condition, as well as individual patient characteristics.
Medical Treatments
Common medical treatments include the use of topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and systemic medications such as antihistamines to manage symptoms like itching. For more persistent cases, phototherapy may be employed to gradually acclimatize the skin to UV exposure and reduce sensitivity.
Advanced Treatments
In recent years, advances in medical technology have introduced newer treatments such as biologics, which target specific pathways in the immune system to control severe reactions. Patients should discuss these options with their dermatologist to determine the most suitable approach for their condition.
Preventing Photodermatoses
Prevention is a key component in managing photodermatoses, and it primarily involves minimizing exposure to triggering factors. Implementing sun protection strategies is essential for reducing the risk of flare-ups.
Sun Protection and Lifestyle Modifications
Effective sun protection strategies include wearing protective clothing such as long sleeves and wide-brimmed hats, using broad-spectrum sunscreens with high SPF, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding certain medications or skincare products that increase photosensitivity, can be beneficial.
By taking these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing sun-induced skin reactions.
Managing Photosensitivity Disorders
Managing photosensitivity disorders requires a combination of daily care routines and long-term strategies to maintain skin health and prevent exacerbations.
Daily Management and Long-term Care
Daily management includes regular application of sunscreen, wearing UV-protective clothing, and avoiding direct sun exposure whenever possible. Long-term care strategies may involve periodic dermatological check-ups to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
Regular consultations with dermatologists can help in tailoring a personalized management plan, ensuring that individuals receive the most effective care for their specific needs.
Sun Allergy vs Photodermatoses
Understanding the distinction between sun allergies and photodermatoses is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. While both conditions involve abnormal reactions to sunlight, they have different underlying mechanisms and presentations.
Key Differences
Sun allergies, such as solar urticaria, are typically acute and manifest quickly with symptoms like hives or welts. In contrast, photodermatoses can be more chronic and varied, with symptoms developing over a longer period and persisting without proper management. Identifying these differences helps in directing patients to the right therapeutic interventions.
Special Considerations
Photodermatoses can have unique implications in certain populations, such as children, and can significantly impact one's quality of life. Addressing these aspects is important for a holistic approach to care.
Photodermatoses in Children and Quality of Life
Children with photodermatoses may require special attention to ensure their activities and lifestyles do not exacerbate their condition. Moreover, the psychological impact of having a visible skin condition should not be underestimated, as it can affect self-esteem and social interactions.
Psychological Aspects
Support from healthcare providers and family is essential in managing the psychological challenges associated with photodermatoses. Providing education and reassurance can help affected individuals cope better with their condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photodermatoses represent a diverse group of skin disorders that require careful management and prevention strategies. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can better navigate their condition and minimize its impact on their lives.
Ongoing research continues to enhance our understanding of these conditions, paving the way for more effective treatments and management strategies. Regular consultations with dermatologists and adherence to preventive measures remain the cornerstone of effective care for individuals with sun-induced skin reactions.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between sun allergy and photodermatoses?
Sun allergies are a subset of photodermatoses characterized by rapid onset of hives after sun exposure, while photodermatoses can vary in symptoms and timing.
Can photodermatoses be cured?
While there is no cure for photodermatoses, symptoms can be managed effectively with appropriate treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
How can I protect my skin if I have photodermatoses?
Protecting your skin involves using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun exposure.
Are there any natural remedies for photodermatoses?
Some natural remedies, such as aloe vera and green tea extracts, may help soothe symptoms, but they should be used in conjunction with medical treatments.
Is photodermatoses hereditary?
Genetic factors can play a role in susceptibility to photodermatoses, and a family history may increase risk.
What should I do if I suspect I have a sun-induced skin condition?
Seek medical advice from a dermatologist to receive a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.