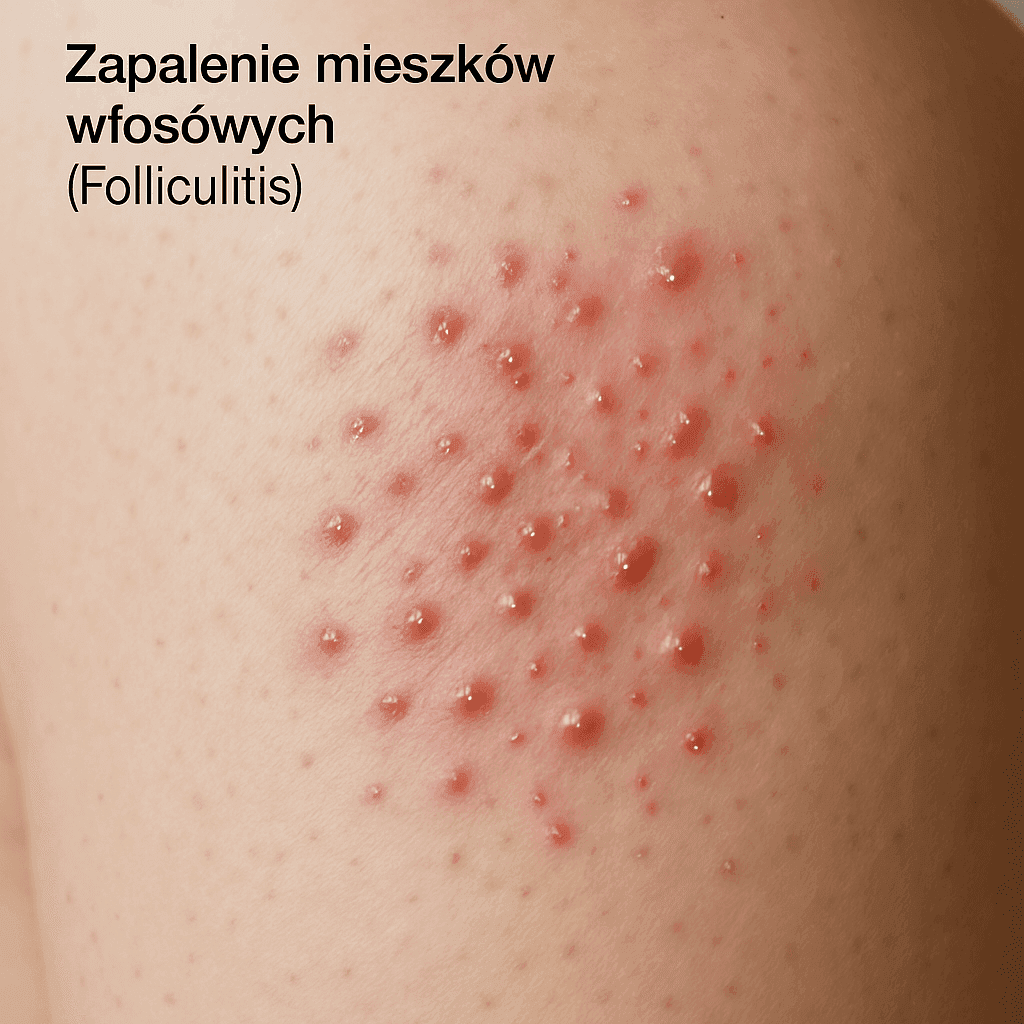
Folliculitis
Causes, symptoms and treatment of folliculitis.
Introduction
Folliculitis, also known as folliculitis, is a common skin condition that involves inflammation of the hair follicles. Although often benign, it can lead to discomfort and complications if not treated properly. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms and treatments for this condition, offering practical tips for those who may be struggling with it.
Causes of folliculitis
Bacteria and viruses
Folliculitis is most often caused by a bacterial infection, usually by Staphylococcus aureus. Viruses, such as the herpes virus, can also lead to this condition. These microorganisms invade the hair follicles, causing inflammation and irritation.
Mechanical and chemical factors
Some mechanical factors, such as rubbing clothing or clothes that are too tight, can lead to damage to the skin, facilitating infection. Chemicals, such as oils or cosmetics, can clog hair follicles, increasing the risk of inflammation.
Impact of personal hygiene
Lack of proper personal hygiene can increase the risk of folliculitis, but over-cleaning the skin is also not recommended. Washing too often removes the skin's natural protective barrier, which can lead to infection.
Symptoms of folliculitis
Folliculitis usually manifests itself as small red or white pustules around the hair follicles. Sometimes they are accompanied by itching or pain. In some cases, pus appears, and the inflammation can spread to larger areas of the skin.
Differences between inflammation and other skin conditions
Often confused with acne, folliculitis is characterized by lesions localized around the hair. Unlike acne, which develops mainly on the face and back, folliculitis can occur on any part of the body covered with hair.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of folliculitis usually involves a physical examination by a dermatologist. In some cases, a sample may need to be taken for microbiological testing to determine the type of infection. Consultation with a doctor is recommended if symptoms are severe, recurrent or do not respond to basic treatment.
Treatment of folliculitis
Pharmacological treatment
Topical or oral antibiotics are most commonly used for bacterial folliculitis. In viral cases, antiviral drugs may be recommended. The dermatologist will choose the appropriate treatment depending on the cause of the infection.
Home treatment
Natural remedies, such as warm compresses, can relieve symptoms. It's a good idea to avoid irritating cosmetics and wear loose clothing. Lifestyle changes, such as improved personal hygiene, can also help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Preventing folliculitis
Preventing folliculitis starts with daily skin care. Washing regularly, but not too often, and using mild cleansers helps keep the skin healthy. Avoiding hot baths, which can dry out the skin, and wearing loose clothing reduces the risk of the condition.
Avoiding risk factors
Avoiding risk factors such as polluted waters, improperly cleaned swimming pools and too-tight clothing can significantly reduce the risk of folliculitis. Taking care of personal hygiene, including changing bedding and towels regularly, is key to prevention.
Folliculitis vs. other conditions
Comparison with acne
While acne is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin, folliculitis is usually a short-term inflammatory condition. Acne often occurs along with the overproduction of sebum and can lead to the formation of blackheads, while folliculitis directly affects the hair follicles.
Differences between bacterial and fungal infections
Bacterial infections most often cause purulent pustules, while fungal infections can manifest as itchy, red patches. Distinguishing between the two is important for choosing the right treatment.
Folliculitis in different groups
Children and adolescents
In children and adolescents, folliculitis often results from increased activity and contact with contaminated surfaces. It is worth paying attention to proper hygiene after sports activities and avoid sharing towels.
Adults and the elderly
In adults, especially the elderly, folliculitis can be associated with compromised immunity or chronic diseases. Regular dermatological examinations and skin care are important in these age groups.
Summary
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that can lead to discomfort, but is usually easy to treat. The key to successful treatment is early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, both pharmacologically and at home. Regular skin care and avoidance of risk factors are key to preventing recurrence.
Sources
- "Dermatology: An Illustrated Colour Text" - Rona M. Mackie
- "ABC of Dermatology" - Paul K. Buxton
- Reliable online sources, such as the websites of dermatological and medical societies.
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to treat folliculitis?
Treatment usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the severity of symptoms and the therapy used.
Is folliculitis contagious?
Although the inflammation itself is not contagious, the bacteria causing the infection can be transmitted, so it is important to follow hygiene rules.