Atypical Moles: When to Consult a Doctor
Learn about atypical moles and when to seek medical advice.
Introduction
Atypical moles, also known as dysplastic nevi, are unusual-looking benign moles that may resemble melanoma, a type of skin cancer. Understanding what atypical moles are and recognizing the signs that differentiate them from normal moles is crucial for early detection and effective management. Early consultation with a healthcare professional can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve skin health outcomes.
What Are Atypical Moles?
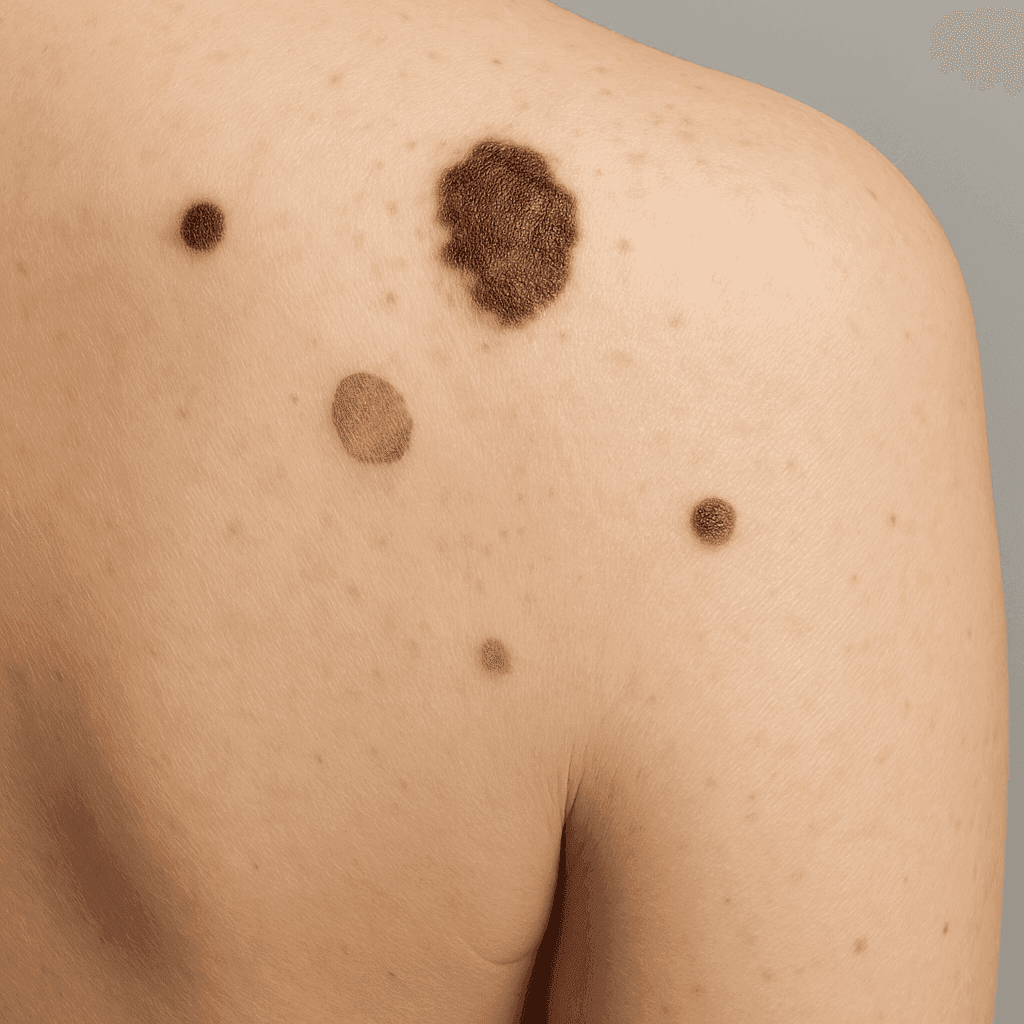
Atypical moles are moles that deviate from the typical appearance of common moles. They often have irregular shapes, varying colors, and indistinct borders. While a normal mole is usually uniform in color and less than 5 millimeters in diameter, atypical moles can be larger and have a mixture of colors. Identifying these characteristics is essential in differentiating them from melanoma, which also presents with irregular features but poses a greater health risk.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition
Family history plays a significant role in the development of atypical moles. If a close relative has atypical moles or a history of melanoma, the likelihood of developing such moles increases. Understanding your family's medical history can be a useful tool in assessing your risk.
Environmental Factors
Sun exposure is a well-documented risk factor for developing atypical moles. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds can induce changes in skin cells, leading to atypical mole formation. Protecting your skin from excessive sun exposure is a critical preventive measure.
Identifying Atypical Moles
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Identifying atypical moles involves being aware of specific signs such as asymmetrical shapes, uneven borders, multiple colors, and a diameter larger than a pencil eraser. These features are critical in differentiating benign moles from potential melanoma.
The ABCDE Rule for Moles
A helpful guideline for identifying atypical moles is the ABCDE rule:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn't match the other.
- Border: Edges are irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined.
- Color: Color varies from one area to another.
- Diameter: Larger than 6 millimeters, though some melanomas can be smaller.
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
When to Consult a Doctor
Indications for Medical Evaluation
If you notice any moles that exhibit the ABCDE characteristics or if there are changes in existing moles, it is important to seek medical advice. Regular skin checks by a healthcare professional can help monitor changes over time and provide peace of mind.
Importance of Regular Skin Checks
Regular self-examinations and annual dermatological check-ups are vital in detecting atypical moles early. Early detection can prevent potential progression to melanoma or aid in timely treatment if necessary.
Diagnostic Procedures
Clinical Examination
During a clinical examination, a dermatologist will inspect the skin for any suspicious moles or changes. This examination is often the first step in assessing the nature of atypical moles.
Dermoscopy and Biopsy
If a mole appears suspicious, further evaluation with dermoscopy—a non-invasive imaging technique—may be employed. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to determine if the mole is benign or malignant.
Treatment Options
Observation and Monitoring
In many cases, atypical moles are monitored over time for any changes. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist ensure that any significant changes are promptly addressed.
Surgical Removal
If a mole poses a risk or shows signs of malignancy, surgical removal may be recommended. This procedure is typically straightforward and performed under local anesthesia.
Prevention and Monitoring
Sun Protection Strategies
Prevention of atypical moles involves minimizing UV exposure. Effective strategies include using broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours.
Regular Dermatological Check-ups
Routine check-ups with a dermatologist are crucial in monitoring any changes in moles and ensuring early detection of potential issues.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the characteristics of atypical moles and recognizing the need for medical consultation are key components of proactive skin health management. Regular monitoring and preventive strategies can reduce the risk of complications. Remember, early detection and intervention are your best defenses against potential skin cancer.
FAQs
What are the warning signs of atypical moles?
Warning signs include asymmetry, uneven borders, multiple colors, a diameter over 6 millimeters, and any changes over time.
How often should I have my moles checked by a dermatologist?
It is recommended to have a full skin examination annually, or more frequently if you have a history of atypical moles or skin cancer.
Can atypical moles turn into melanoma?
While atypical moles themselves are benign, they can indicate an increased risk of melanoma, necessitating regular monitoring.
Is it necessary to remove all atypical moles?
Not all atypical moles require removal. Decisions are based on risk assessment, changes in the mole, and clinical judgment.
How can I reduce my risk of developing atypical moles?
Reduce sun exposure, use adequate sun protection, and have regular skin checks.
Are atypical moles common in children?
While less common, atypical moles can occur in children, particularly those with a family history of melanoma. Regular monitoring is advised.