Autoimmune Skin Diseases: Overview and Symptoms
Comprehensive look at autoimmune skin conditions.
Introduction
Autoimmune skin diseases are conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to various dermatological issues. These diseases can manifest in different forms, each affecting the skin's appearance and function in unique ways. Understanding these conditions is crucial as they can significantly impact quality of life. While some autoimmune skin diseases are mild, others can be severe and require ongoing medical attention.
Autoimmune skin conditions are not only complex due to their diverse manifestations but also because of their unpredictable nature. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying mechanisms can aid in managing these conditions effectively. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of autoimmune skin diseases, their symptoms, causes, and management strategies.
Types of Autoimmune Skin Diseases
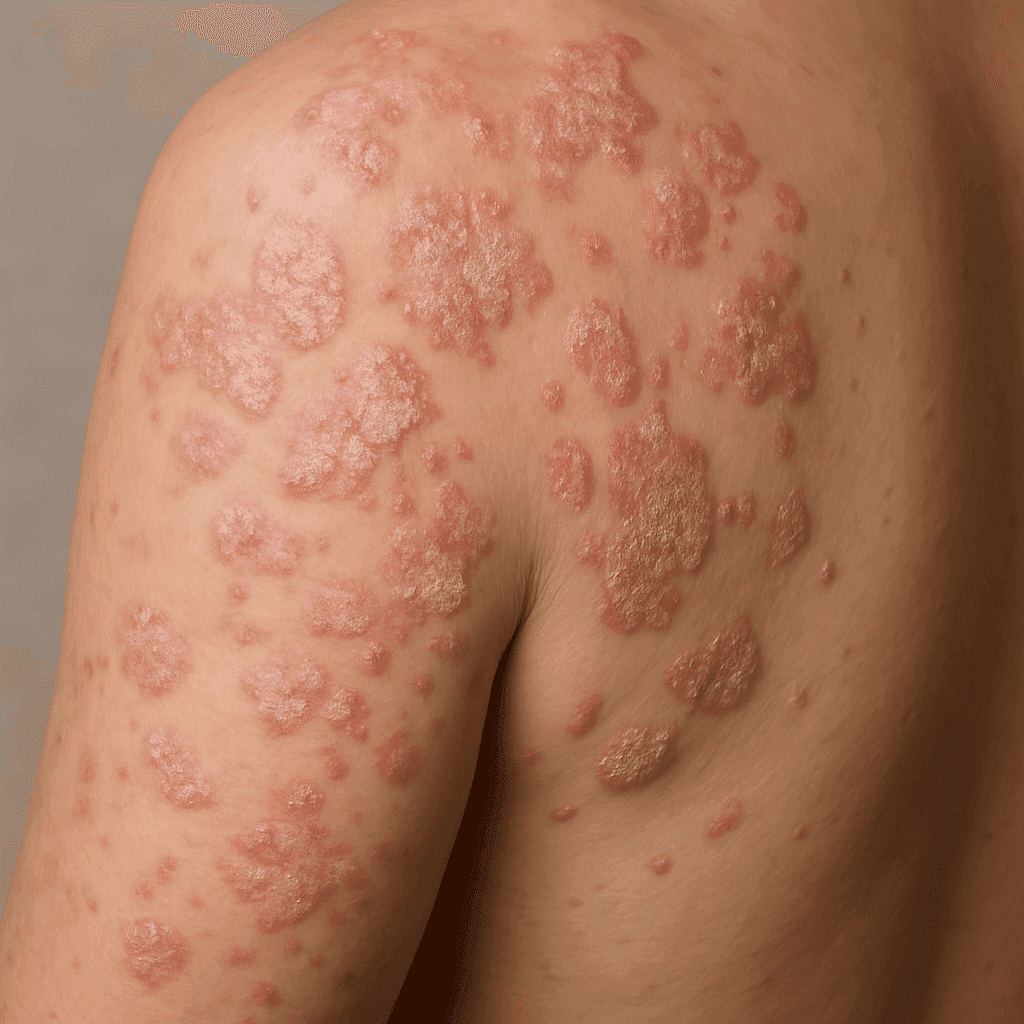
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a common autoimmune skin disease characterized by red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. These patches are often found on the elbows, knees, and scalp but can appear anywhere on the body. The severity of psoriasis can range from minor irritation to severe disfigurement, and it often requires a comprehensive treatment approach.
Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs, including the skin. Cutaneous lupus presents as a rash, typically on sun-exposed areas like the face and neck. The rash can be butterfly-shaped across the cheeks and nose, a hallmark feature of systemic lupus.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo involves the loss of skin pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. It occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin color, are destroyed by the immune system. While it is not life-threatening, vitiligo can have profound psychological effects due to changes in appearance.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is characterized by the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. It can be localized or systemic, with the latter affecting internal organs as well. The skin may become shiny, and mobility can be restricted due to the stiffness.
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an inflammatory disease marked by muscle weakness and a distinctive skin rash. The rash is typically red or violet and appears on the face, knuckles, and elbows. Muscle weakness often accompanies the rash, leading to further complications if untreated.
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare autoimmune disease causing blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. These blisters are fragile and can rupture easily, leading to painful skin erosions. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent severe complications.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Skin Diseases
Common Symptoms
Autoimmune skin diseases share several common symptoms, including skin rashes, redness, and swelling. Itching and pain are also frequently reported, impacting daily activities and quality of life. These symptoms can vary significantly in intensity and duration, depending on the specific condition.
Specific Symptoms by Disease Type
Each autoimmune skin disease has unique symptoms. For example, psoriasis is known for its scaly patches, while vitiligo is characterized by depigmented areas. Recognizing these distinct symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. Individuals may also experience systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and joint pain, particularly in conditions like lupus.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of autoimmune skin diseases. A family history of autoimmune conditions can increase the likelihood of developing similar issues. Researchers continue to explore specific genetic markers associated with these diseases to better understand their origins.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors, such as UV exposure, infections, and chemical exposure, can trigger or exacerbate autoimmune skin diseases. These triggers can vary from person to person, making it essential to identify and manage them to prevent flare-ups.
Role of the Immune System
In autoimmune skin diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own skin cells. This misguided response leads to inflammation and other symptoms. Understanding the immune system's role is key to developing effective treatments and management strategies.
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Skin Diseases
Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination by a dermatologist is the first step in diagnosing autoimmune skin diseases. The dermatologist will assess the skin's appearance, ask about symptoms, and review the patient's medical history to identify patterns indicative of autoimmune conditions.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, including blood tests, can help detect specific antibodies associated with autoimmune diseases. These tests are crucial for confirming a diagnosis and ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Biopsy Procedures
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to examine the affected tissue under a microscope. This procedure provides valuable information about the presence of autoimmune activity and helps guide treatment decisions. The biopsy is typically performed under local anesthesia, minimizing discomfort for the patient.
Treatment and Management
Medications
Medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms and control the immune response. These can include topical treatments, oral medications, and biologics that target specific parts of the immune system.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, avoiding known triggers, and maintaining a healthy routine, can significantly impact the management of autoimmune skin diseases. Regular exercise and adequate sleep are also beneficial.
Role of Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a critical role in managing autoimmune skin conditions. Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce flare-ups and maintain skin health.
Managing Stress
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga, can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Chronic stress is known to exacerbate autoimmune conditions, making effective stress management a crucial part of treatment.
Living with Autoimmune Skin Diseases
Coping Strategies
Living with an autoimmune skin disease requires effective coping strategies. Building a support network, seeking therapy, and staying informed about the condition can empower individuals to manage their disease more effectively.
Support and Resources
Support groups and online resources can provide valuable information and emotional support. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can reduce feelings of isolation and offer practical advice for daily management.
Autoimmune Skin Diseases in Different Populations
Children
Autoimmune skin diseases can also affect children, often presenting differently than in adults. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent long-term complications and support healthy development.
Adults
In adults, autoimmune skin diseases might manifest more severely, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach to management. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the disease's progression.
Gender Differences
Research indicates that some autoimmune skin diseases are more prevalent in women, possibly due to hormonal influences. Understanding these differences can help tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
FAQs
What are the most common autoimmune skin diseases?
Common autoimmune skin diseases include psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, vitiligo, and scleroderma. Each has distinct symptoms and requires specific management strategies.
How are autoimmune skin diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination, laboratory tests, and sometimes skin biopsies to confirm the presence of an autoimmune process.
Can diet affect autoimmune skin conditions?
Yes, diet can significantly impact the management of autoimmune skin conditions. Anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce symptoms and flare-ups.
Are autoimmune skin diseases hereditary?
There is a genetic component to many autoimmune skin diseases, meaning they can run in families. However, environmental factors also play a significant role.
What is the role of stress in autoimmune skin diseases?
Stress can exacerbate autoimmune skin diseases, making stress management an important part of treatment. Techniques such as meditation and yoga can be beneficial.
How can autoimmune skin diseases be managed effectively?
Effective management involves a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and stress management. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to tailor the treatment plan.