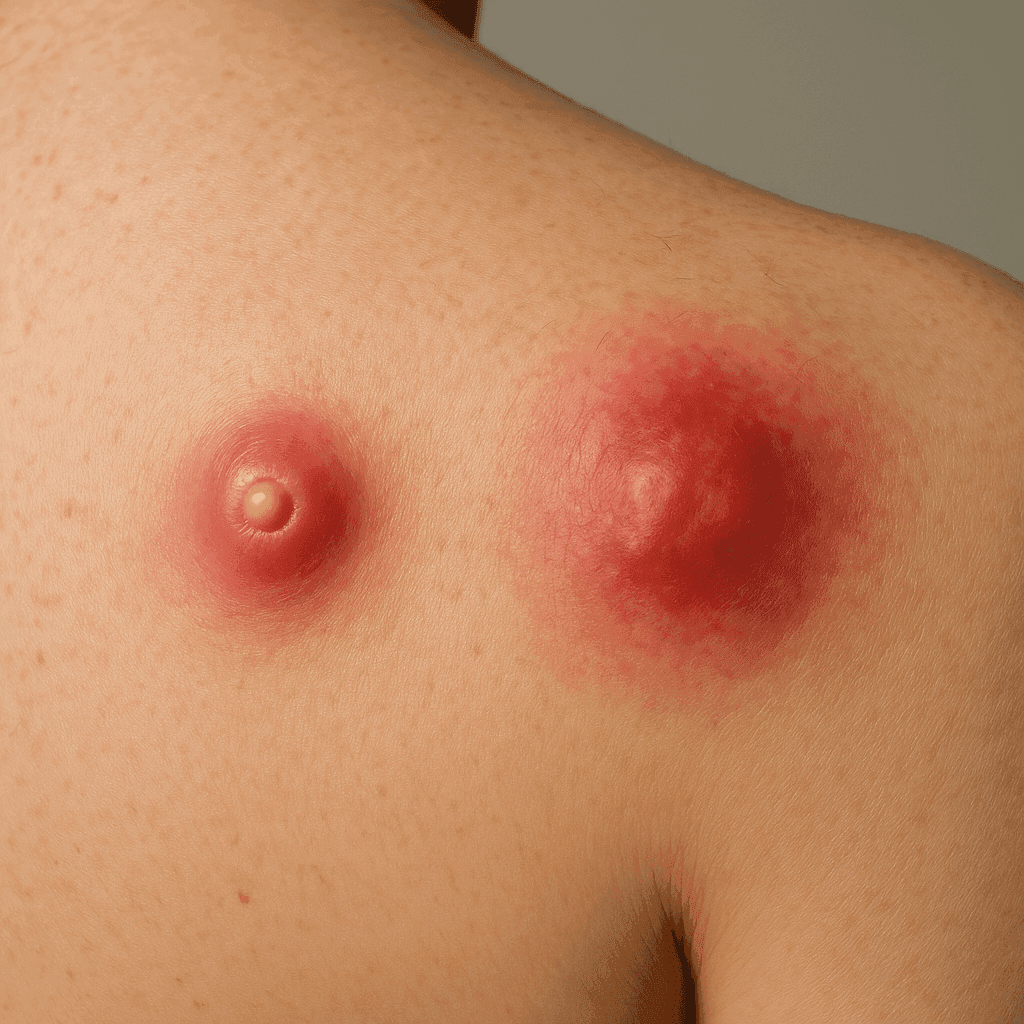
Boil vs. Abscess: Differences and How to Treat
Understand boils and abscesses, their causes, and treatments.
Introduction
Skin infections can be both painful and concerning. Among the most common are boils and abscesses. Both conditions involve pus-filled lumps on the skin, but they have different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and prevention. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of boils and abscesses, helping you recognize symptoms and understand treatment options.
What is a Boil?
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a painful, pus-filled bump that forms under the skin when bacteria infect and inflame one or more hair follicles. They typically appear as red, swollen lumps that may eventually fill with pus and grow larger over a few days. Common causes include bacterial infections, particularly by Staphylococcus aureus, and can occur anywhere on the body, often in areas prone to sweat or friction like the armpits or thighs.
Symptoms of a Boil
Boils usually start as small, red, painful lumps. Over time, they grow larger and more painful as they fill with pus. They may develop a white or yellow center (head) that can eventually rupture, allowing the pus to drain out. Other symptoms can include itching, and in some cases, fever or swollen lymph nodes in nearby areas.
What is an Abscess?
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. It is typically a deeper skin infection than a boil and can occur in any part of the body. Abscesses are often the result of bacterial infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common cause. They can form in response to blocked sebaceous glands or minor breaks and punctures in the skin.
Symptoms of an Abscess
Abscesses appear as swollen, pus-filled lumps that are often red, warm to the touch, and painful. Unlike boils, which are usually smaller, abscesses can become quite large and may require medical intervention to drain effectively. Other symptoms can include fever, swelling, and a feeling of malaise.
Boil vs. Abscess: Key Differences
While boils and abscesses may appear similar, there are key differences between them. Boils are usually smaller and appear on the surface of the skin, whereas abscesses are deeper infections that can grow larger and affect underlying tissues. Boils typically occur in hair follicles, while abscesses can develop in any tissue. Symptoms may overlap, but abscesses often cause more systemic symptoms like fever and fatigue.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes of Boils
Boils are primarily caused by bacterial infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common culprit. Factors that increase the risk of developing boils include poor hygiene, close contact with someone who has a boil, and conditions like diabetes that affect the immune system.
Common Causes of Abscesses
Abscesses are usually caused by bacterial infections, but they can also result from fungi or parasites. Risk factors include compromised immunity, chronic skin conditions, and exposure to unsanitary environments.
Risk Factors for Both
Both boils and abscesses are more likely to occur in individuals with weakened immune systems, poor hygiene practices, or skin injuries. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and eczema also increase the risk.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Boils
When diagnosing a boil, doctors typically perform a physical examination and may take a sample of the pus to identify the bacteria causing the infection. This helps determine the appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Procedures for Abscesses
For abscesses, doctors may use imaging tests like ultrasounds or CT scans to assess the extent of the infection. A sample of the pus may also be taken for laboratory analysis to guide treatment.
Treatment Options
Home Remedies for Boils
For small boils, home treatments are often effective. Applying warm compresses several times a day can help reduce pain and promote drainage. Over-the-counter pain relievers and topical antibiotics can also be beneficial.
Medical Treatments for Boils
If a boil does not improve with home treatment, medical intervention may be necessary. This can include incision and drainage performed by a healthcare professional, and in some cases, antibiotic therapy if the infection is severe.
Home Remedies for Abscesses
While small abscesses might respond to warm compresses and good hygiene, more persistent or larger abscesses often require medical attention. Natural remedies, such as tea tree oil, may offer some benefit but should not replace professional care.
Medical Treatments for Abscesses
Surgical drainage is often necessary for larger abscesses. This procedure involves making a small incision to allow the pus to drain. In addition, antibiotic treatments may be prescribed to combat the underlying infection.
Prevention Tips
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is crucial in preventing boils and abscesses. Regular handwashing, using antibacterial soap, and keeping wounds clean and covered can reduce your risk.
Lifestyle Changes
To prevent recurrence, consider lifestyle changes such as wearing loose, breathable clothing, maintaining a healthy diet to boost your immune system, and avoiding sharing personal items like towels or razors.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect a boil or abscess is not healing or is getting worse, it's essential to seek medical advice. Warning signs include a high fever, spreading redness, or severe pain. Early intervention can prevent complications.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a boil and an abscess?
Boils are superficial skin infections, whereas abscesses are deeper infections that can become larger and affect underlying tissues.
Can a boil turn into an abscess?
Yes, if a boil is not treated properly, it can deepen and develop into an abscess.
How long does it take for a boil to heal?
Boils typically heal within two weeks, especially with proper care.
Are boils contagious?
Boils themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria causing them can spread.
What should I do if my abscess keeps returning?
Recurrent abscesses should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine underlying causes and appropriate treatments.
Can I pop a boil or abscess at home?
It is not recommended to pop boils or abscesses at home, as this can worsen the infection or cause scarring.