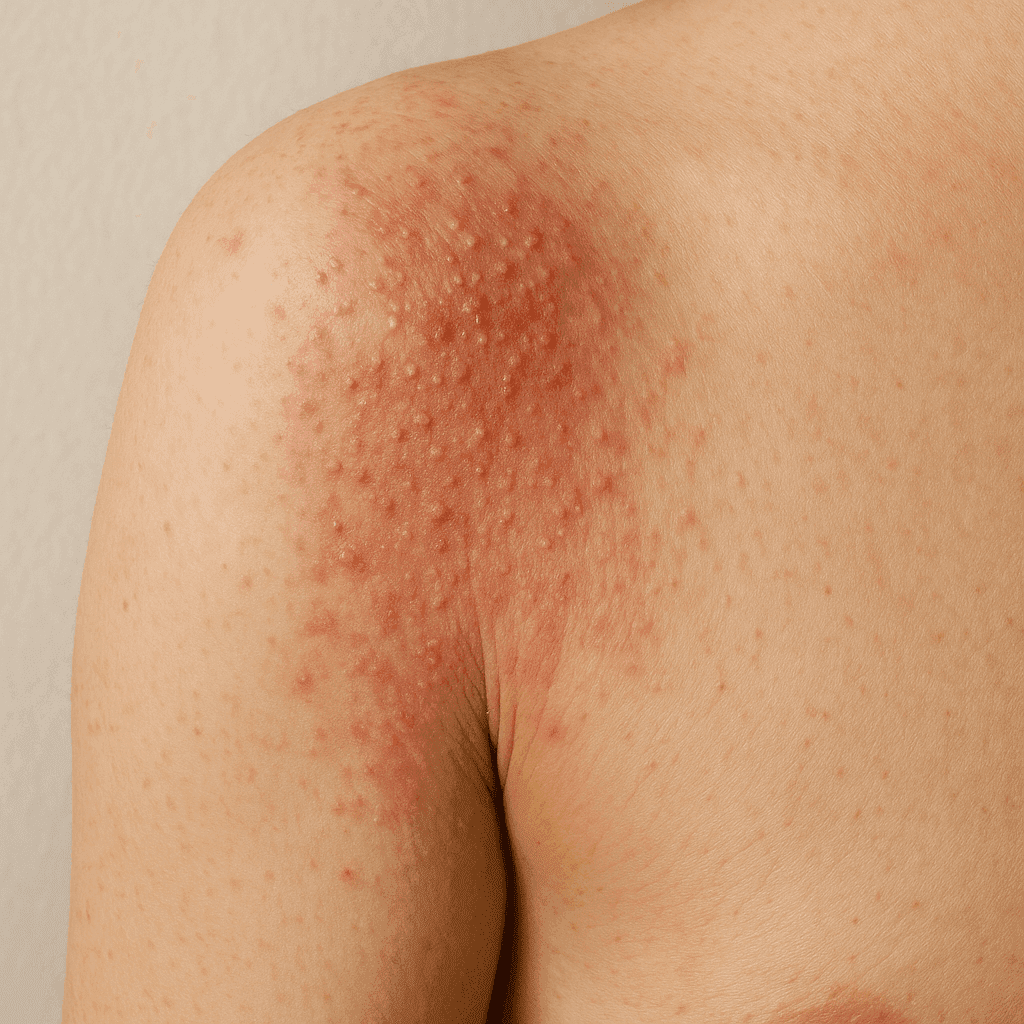
Contact Dermatitis.
Introduction
Contact eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that occurs as a result of contact with an irritant or allergen. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, and manifests with a variety of symptoms ranging from mild redness to itchy blisters. There are two main types of contact eczema: allergic and irritant. Allergic contact eczema is a reaction of the immune system to allergens such as nickel or latex, while irritant eczema results from direct damage to the skin by chemical or physical substances.
Causes of contact eczema
Allergic contact eczema
Allergic contact eczema is caused by the immune system's reaction to a substance that the body recognizes as harmful. Common allergens include metals, dyes, preservatives and latex. Contact with these substances can lead to a delayed allergic reaction, meaning that symptoms can appear even days after exposure.
Irritant contact eczema
This type of eczema occurs as a result of direct damage to the skin from chemical or physical substances, such as detergents, solvents, or prolonged contact with water. Irritant contact eczema is the most common type of eczema and can occur after just one contact with an irritant.
Environmental and occupational factors
Workplace factors can significantly increase the risk of contact eczema. Workers in the chemical industry, hairdressers, medics or those working in agriculture are particularly vulnerable to contact with irritants. Understanding and identifying potential risk factors is key to prevention.
Symptoms of contact eczema
How do you recognize contact eczema?
Contact eczema symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the reaction and the type of eczema. Redness, itching, blistering and flaking of the skin are common. In the case of allergic contact eczema, symptoms may also include swelling and rashes that appear at the site of contact with the allergen.
Differences between allergic and irritant symptoms
Symptoms of irritant contact eczema usually appear faster than those of allergic contact eczema and mainly include swelling, redness and burning. Allergic contact eczema develops more slowly and manifests as a more extensive rash that can spread beyond the area of direct contact.
Diagnostics
Skin and allergy tests
The diagnosis of contact eczema often includes skin tests to help identify substances that cause an allergic reaction. The patch test is one of the most commonly used tests, which involves applying small amounts of potential allergens to the skin and observing the reaction. This allows you to determine precisely what is causing the allergy.
When to see a doctor?
If eczema symptoms persist for a long time or are very bothersome, it is worth consulting a dermatologist. The specialist will help identify the causes and suggest appropriate treatment. It is also worth seeing a doctor if eczema appears in areas that can easily become infected.
Treatment of contact eczema
Pharmacological treatment
Treatment of contact eczema depends on its severity and causes. For more severe reactions, doctors may prescribe steroid ointments to help reduce inflammation. Antihistamines can also be used to relieve itching.
Home remedies and natural remedies
In milder cases, home remedies such as cold compresses to relieve itching and oatmeal baths can be helpful. Avoiding triggers and using mild, fragrance-free skin care products can also provide relief.
The importance of avoiding triggers
The key to successful contact eczema management is avoiding contact with triggers. Identifying and eliminating allergens or irritants from daily life can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
Contact eczema in different groups
Contact eczema in children
Children are particularly susceptible to contact eczema due to their more delicate skin and more frequent contact with a variety of irritants. It is important for parents to keep a close eye on their child's skin and avoid potential allergens.
Contact eczema in adults
In adults, contact eczema is often associated with occupational and environmental factors. People who work in conditions of increased exposure to chemicals should take special care to protect their skin and use appropriate personal protective equipment.
Impact on quality of life
Contact eczema can significantly affect quality of life, causing physical and psychological discomfort. Itching, pain and visible skin lesions can lead to reduced self-esteem and limitations in daily functioning.
Prevention
How to avoid contact eczema?
Avoiding contact eczema requires identifying and eliminating irritants and using appropriate skin protection. People with allergies should carefully read product labels and avoid known allergens.
Importance of diet and lifestyle
A healthy diet and lifestyle can support overall skin health. Including foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids in the diet can help strengthen the skin barrier.
The role of patient education
Patient education plays a key role in the prevention and treatment of contact eczema. Awareness of triggers and effective treatments can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by the condition.
Summary
Contact eczema is a common condition that can affect anyone. The key to managing this condition is to avoid triggers, identify symptoms promptly and apply appropriate treatments. In severe or persistent cases, consultation with a doctor is recommended.
FAQ
Frequently asked questions about contact eczema
-
**Is contact eczema contagious?**No, contact eczema is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
-
**How long does it take to treat contact eczema?**Treatment time depends on the severity of symptoms and the effectiveness of avoiding triggers. Treatment can last from a few days to several weeks.