Folliculitis (Hair Follicle Inflammation): Causes and Treatment
Understand folliculitis causes and treatments.
Introduction
Folliculitis, a common skin condition, occurs when hair follicles become inflamed. This often results from bacterial or fungal infections, physical irritation, and other factors. Understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively and preventing its recurrence.
What is Folliculitis?
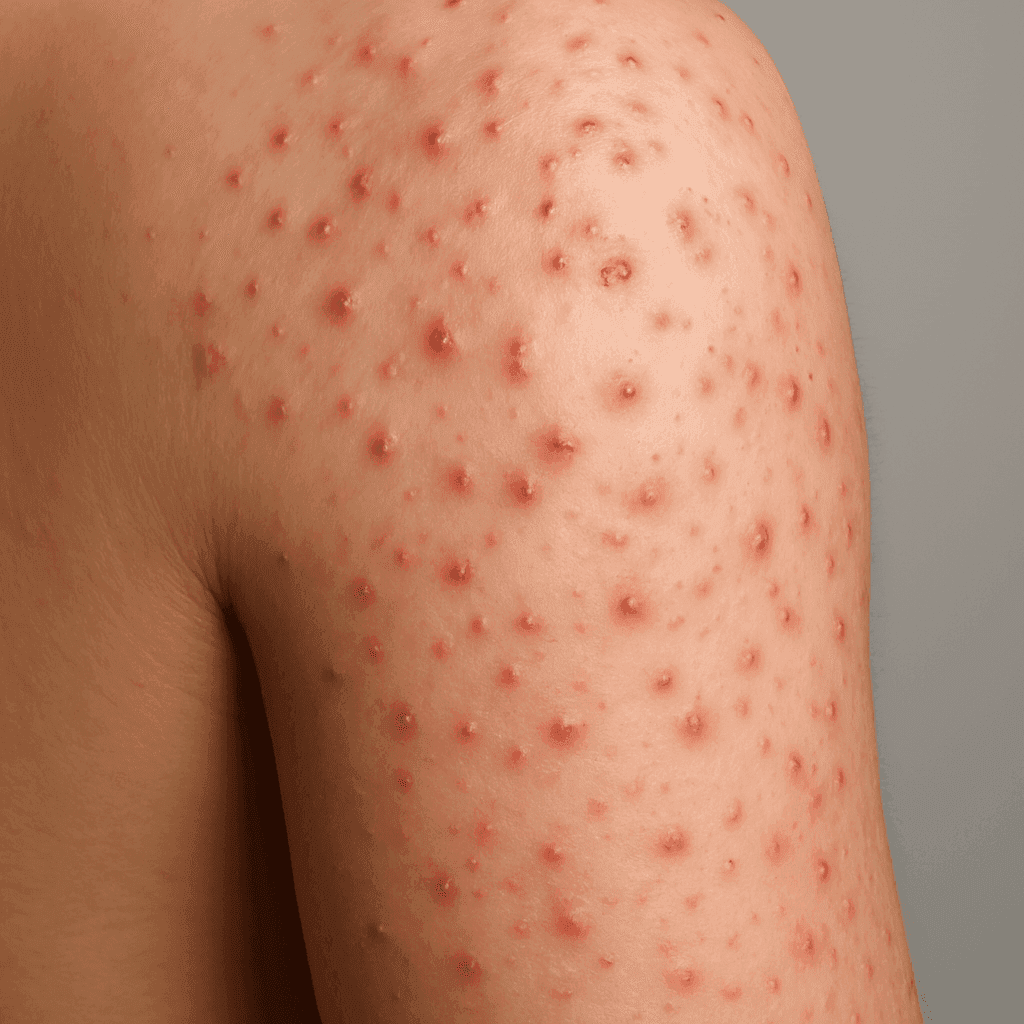
Folliculitis is the inflammation of hair follicles, appearing as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles. It can affect any part of the body where hair grows. There are several types of folliculitis, including bacterial, fungal, viral, and non-infectious forms, each with distinct causes and treatments.
Causes of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can be caused by bacterial infections, often involving Staphylococcus aureus. Viral infections, such as herpes simplex, can also lead to folliculitis. Fungal infections, including those caused by Malassezia species, are another cause. Physical irritants, like shaving or waxing, can damage hair follicles, leading to inflammation. Additionally, underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or compromised immune systems, can increase susceptibility.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Common symptoms include itchy, burning skin, and clusters of red bumps or pus-filled blisters around hair follicles. The symptoms can vary depending on the type of folliculitis. For example, fungal folliculitis often leads to more persistent itching, while bacterial folliculitis might present with pus-filled lesions.
Diagnosis of Folliculitis
A clinical examination by a healthcare professional is often sufficient to diagnose folliculitis. In some cases, laboratory tests, such as cultures or skin biopsies, may be necessary to identify the exact cause of the inflammation. These tests help in determining the appropriate treatment and ruling out other similar conditions.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis
Medical Treatments
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Bacterial folliculitis often requires antibiotics, either topical or oral. Antifungal medications are prescribed for fungal infections, while antiviral treatments address viral causes. In some cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Home remedies can be effective for mild cases. Warm compresses may alleviate discomfort, and antibacterial soaps can help prevent infection. Natural treatments, such as tea tree oil, have antimicrobial properties that might benefit some patients.
Preventing Folliculitis
Preventing folliculitis involves proper skincare and hygiene practices. Using clean razors, moisturizing the skin, and avoiding tight clothing can reduce irritation. Maintaining a regular skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, can help keep hair follicles clear and healthy.
Complications of Folliculitis
If left untreated, folliculitis can lead to complications such as scarring or permanent hair loss. Recurrent episodes can result in chronic folliculitis, requiring more intensive management strategies. Early treatment and proper skin care are essential to prevent these outcomes.
Folliculitis vs. Other Skin Conditions
Folliculitis can be confused with other skin conditions like acne or dermatitis. Unlike acne, which primarily affects the oil glands, folliculitis specifically involves hair follicles. Understanding these differences is important for effective treatment and management.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to treat folliculitis at home?
Home treatments include warm compresses and antibacterial soaps. If symptoms persist, consult a healthcare provider.
Can folliculitis go away on its own?
Mild cases of folliculitis may resolve without treatment, but persistent or severe cases require medical attention.
Is folliculitis contagious?
While some forms can be spread through skin contact, not all types are contagious. Practice good hygiene to prevent transmission.
How can I prevent folliculitis after shaving?
Use a sharp razor, shave in the direction of hair growth, and apply moisturizing lotion to reduce irritation and prevent folliculitis.
Are there any long-term effects of untreated folliculitis?
Potential complications include scarring and chronic inflammation. Early treatment helps prevent these issues.
Can children get folliculitis?
Yes, children can develop folliculitis. It's important to monitor symptoms and consult a healthcare provider for appropriate care.