Fungal Skin Infections: Types and Effective Therapies
Explore types and treatments for fungal skin infections.
Introduction
Fungal skin infections are common ailments affecting millions of individuals worldwide. These infections can range from mild to severe and can cause significant discomfort. Understanding the types of fungal skin infections and the treatments available is crucial for effective management and relief.
Fungal infections of the skin are caused by various fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. These microorganisms thrive in warm, moist environments and can easily spread through direct contact. Early identification and treatment are essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Types of Fungal Skin Infections
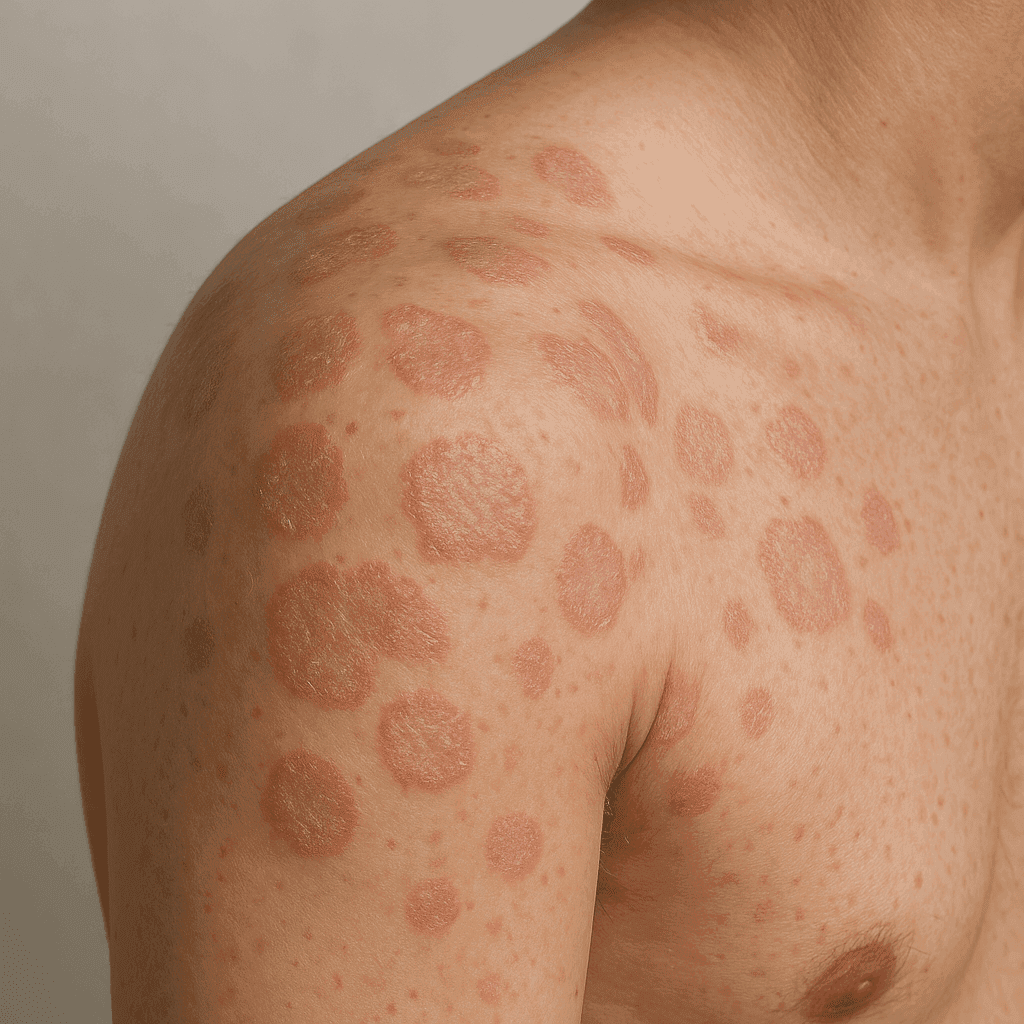
Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
Ringworm is a common fungal infection characterized by a red, circular rash with a clearer center, giving it a ring-like appearance. It is not caused by a worm but by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. Risk factors include close contact with infected individuals or animals, sharing personal items, and living in warm, humid environments.
Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete's foot primarily affects the feet, particularly the spaces between the toes. Symptoms include itching, burning, and peeling skin. It is often contracted in communal areas such as locker rooms and pools, where the warm, moist conditions promote fungal growth.
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
Jock itch occurs in the groin area and is more common in males. It presents as a red, itchy rash that may be ring-shaped. Factors such as excessive sweating, tight clothing, and damp environments increase the risk of jock itch.
Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis)
Nail fungus affects the nails, causing them to become thick, discolored, and brittle. It is challenging to treat due to the protective barrier of the nail, which makes medication penetration difficult. Treatment often requires prolonged use of antifungal agents.
Yeast Infections (Candidiasis)
Yeast infections are caused by the overgrowth of Candida species, commonly affecting moist areas such as the armpits and groin. Symptoms include red, itchy patches and white, curd-like discharge in some cases.
Diagnosing Fungal Skin Infections
Accurate diagnosis of fungal skin infections is essential for effective treatment. Dermatologists often use visual examination and may take skin scrapings for microscopic analysis or culture to identify the specific fungus involved. Early diagnosis can prevent the spread of infection and reduce the risk of complications.
In some cases, additional tests such as Wood's lamp examination or biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation if a fungal infection is suspected.
Effective Therapies for Fungal Skin Infections
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments are often the first line of treatment for mild fungal infections. Popular options include clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine. These products should be applied as directed, typically for several weeks, to ensure complete eradication of the fungus.
Prescription Medications
For more severe or persistent infections, prescription medications may be necessary. Oral antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, are often prescribed when topical treatments are insufficient. A healthcare provider can determine when prescription medication is appropriate.
Natural Remedies
Some individuals prefer natural remedies, such as tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar, which are believed to have antifungal properties. While these remedies may offer relief, their efficacy varies, and they should be used with caution. Consulting a healthcare provider is advisable before trying home-based treatments.
Preventing Fungal Skin Infections
Prevention of fungal skin infections involves maintaining good hygiene and making lifestyle adjustments. Key preventive measures include:
- Keeping skin dry and clean
- Wearing breathable fabrics
- Avoiding sharing personal items such as towels and razors
- Using antifungal powders in shoes
Environmental precautions, such as wearing flip-flops in communal showers and pools, can also reduce the risk of infection.
Managing Chronic Fungal Infections
Chronic fungal infections may require long-term management strategies. Regular monitoring and adjusting treatment plans are crucial to prevent recurrence. In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as weight loss or dietary adjustments, may help in managing chronic conditions.
Patients with chronic fungal infections should maintain open communication with their healthcare providers to ensure effective management and address any concerns promptly.
FAQs
What are the first signs of a fungal skin infection?
Initial signs include itching, redness, and a rash. Some fungal infections may also cause peeling or cracking skin.
Can fungal skin infections go away on their own?
While minor infections may resolve, treatment is usually necessary to prevent spread and recurrence.
How can I tell if my skin infection is fungal or bacterial?
Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for accurate diagnosis, as symptoms can be similar.
Are there any side effects to antifungal medications?
Side effects may include skin irritation or gastrointestinal issues. It is important to follow the prescribed regimen and report any adverse effects to a healthcare provider.
What should I do if over-the-counter treatments don't work?
If symptoms persist, seek medical advice for potential prescription treatments or further evaluation.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent recurrent fungal infections?
Yes, adopting preventive measures such as improved hygiene and wearing appropriate clothing can reduce recurrence.