Hives (Urticaria): Causes, Symptoms and When to See a Doctor
Understand hives: causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Introduction
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts. These welts vary in size and can appear suddenly anywhere on the body. Understanding the causes and symptoms of hives is essential for effective management and treatment. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on hives, including the differences between acute and chronic forms, and when it is necessary to seek medical advice.
What Are Hives?
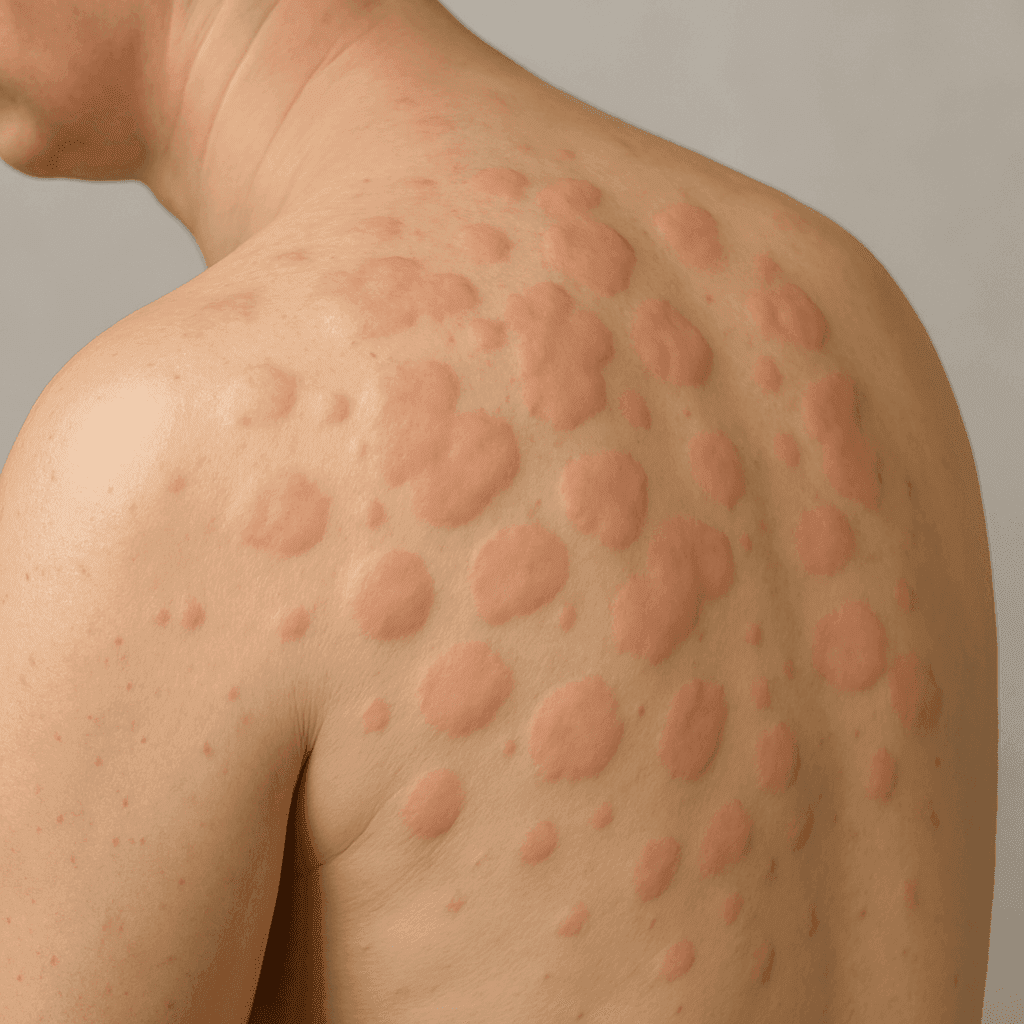
Hives are a reaction in which the skin develops itchy, raised welts. They can be acute, lasting less than six weeks, or chronic, persisting for more than six weeks. Acute hives are often triggered by allergic reactions, while chronic hives may be associated with underlying health conditions or unknown causes. The welts may vary in size and can join together to form large patches. Hives can affect any part of the body and may be accompanied by a burning or stinging sensation.
Causes of Hives
Hives can arise from a variety of triggers. Common allergens include foods such as nuts, shellfish, and eggs, as well as insect stings and medications. Stress and emotional factors can also trigger hives, as can physical stimuli like extreme temperatures and pressure. Additionally, hives can be a symptom of underlying health conditions, such as thyroid disease or lupus. Identifying the trigger is crucial for managing and preventing future outbreaks.
Symptoms of Urticaria
The primary symptom of hives is the appearance of red or skin-colored welts that are often itchy. These welts can change shape, disappear, and reappear within minutes or hours. Unlike other skin conditions, hives do not have a scaly appearance, and they typically blanch (turn white) when pressed. It's important to differentiate between hives and other conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, which have distinct characteristics.
Diagnosis of Hives
If you experience hives, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional, especially if the condition persists or is accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing. A doctor may perform a physical examination and review your medical history to identify possible triggers. In some cases, allergy tests or blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Hives
Medical Treatments
For immediate relief from hives, antihistamines are commonly prescribed to reduce itching and swelling. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to decrease inflammation. Other medications, such as leukotriene modifiers, can be considered for chronic hives.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Natural treatments include applying cool compresses and taking soothing baths with colloidal oatmeal. It's also beneficial to avoid known triggers and manage stress through relaxation techniques. Keeping a diary to track outbreaks can help identify triggers and prevent future occurrences.
Chronic Hives: Management and Treatment
Long-term management of chronic hives focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. This includes a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider. Coping mechanisms such as mindfulness and stress reduction are vital components in managing chronic hives.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of hives are mild and resolve on their own, certain signs warrant medical attention. Seek a doctor’s advice if hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or lips, or if they do not improve with over-the-counter treatments. Being prepared for your appointment by noting down symptoms and potential triggers can aid in diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention Tips for Hives
Preventing hives involves lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding known allergens and irritants. Dietary considerations, like eliminating foods that trigger hives, can also be beneficial. Ensuring a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall skin health and reduce the likelihood of hives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hives
- Can stress alone cause hives? Yes, stress is a known trigger for hives, although it often acts in conjunction with other factors.
- Are hives contagious? No, hives are not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
- How can I tell if my hives are serious? If hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling in the throat, or do not respond to treatment, seek immediate medical attention.
- What foods are most likely to trigger hives? Common food triggers include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and certain additives.
- Is it possible for hives to go away on their own? Yes, many cases of hives resolve spontaneously without treatment.
- Can hives be a sign of something more serious? Persistent or severe hives may indicate an underlying health issue and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.