Molluscum Contagiosum in Children: Causes and Treatment
Understanding molluscum contagiosum in children.
Introduction
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection in children, characterized by small, painless bumps on the skin. Understanding this condition is crucial for parents and caregivers, as it helps in managing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
The importance of recognizing and addressing molluscum contagiosum lies in its potential to spread among children, especially in communal settings like schools and daycares. This article provides an overview of the condition, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
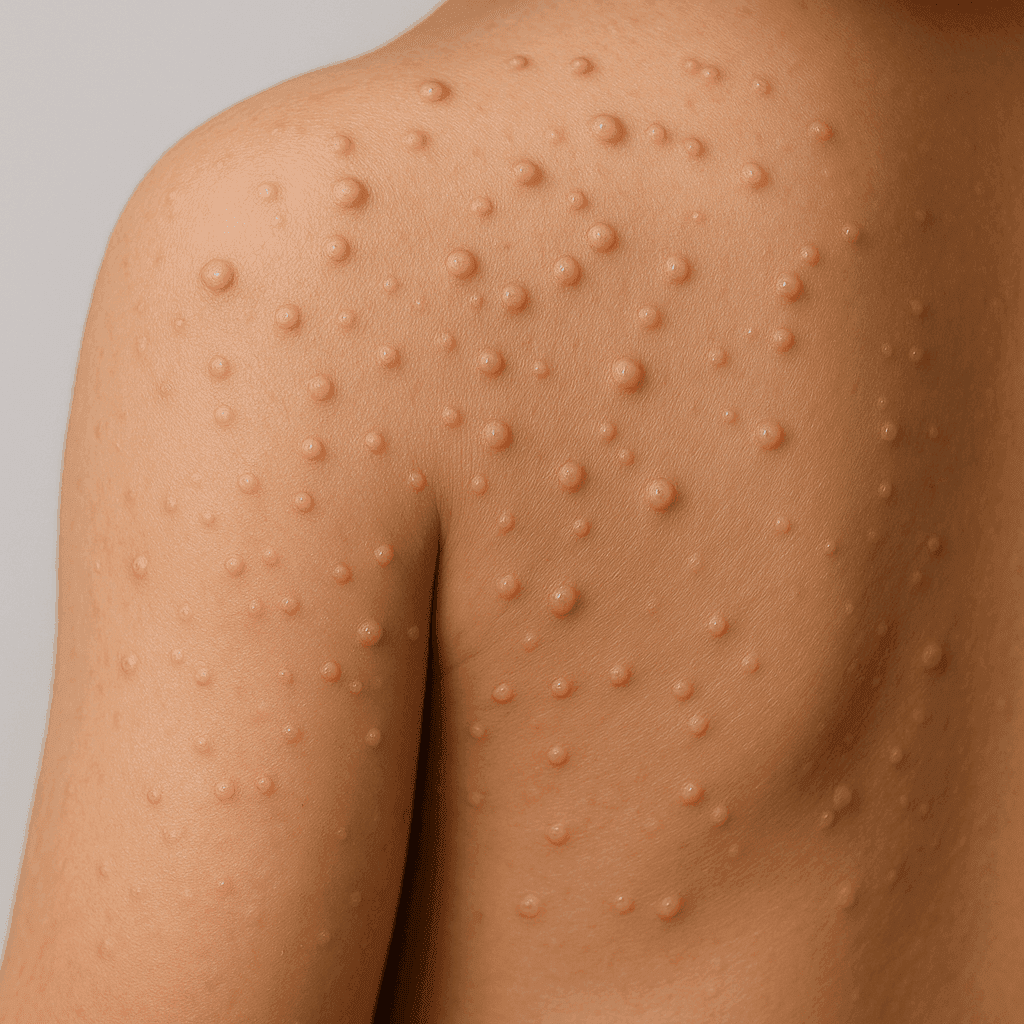
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin condition caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a member of the poxvirus family. It presents as small, firm, raised lesions that are usually flesh-colored and have a dimple in the center.
How it Affects the Skin
The virus infects the outer layer of the skin, leading to the development of lesions that can appear anywhere on the body. Although the bumps are generally painless, they can become itchy or irritated, especially if scratched.
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
Viral Origin
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus that is highly contagious, particularly among children. It spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact or by touching contaminated objects such as towels, toys, or clothing.
Transmission Methods
Children can contract the virus through close physical contact during play or sports. Sharing personal items like towels or grooming tools can also facilitate the spread. The virus thrives in warm, humid environments, making swimming pools and bathhouses common sites of transmission.
Risk Factors for Children
Children with weakened immune systems or eczema are more susceptible to molluscum contagiosum. Additionally, children who live in crowded conditions or attend group activities are at higher risk.
Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
Common Signs to Look For
The primary symptom is the appearance of small, round bumps on the skin. These lesions are usually flesh-colored and have a central dimple. They can appear anywhere but are most commonly found on the face, neck, arms, and hands.
How to Differentiate from Other Skin Conditions
Unlike other skin rashes, molluscum contagiosum lesions are distinct due to their central dimple. However, they can be confused with warts or chickenpox, making professional diagnosis important if there is any doubt.
Diagnosis of Molluscum Contagiosum
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect your child has molluscum contagiosum, it's important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. This is particularly crucial if the bumps change in appearance, become painful, or are located in sensitive areas like the eyes.
Diagnostic Procedures
A dermatologist can usually diagnose molluscum contagiosum through a physical examination. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Molluscum Contagiosum
Medical Treatments
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams and ointments can help reduce lesions.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the bumps with liquid nitrogen.
- Curettage: A procedure to scrape away the lesions.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
While medical treatments are effective, some home remedies like tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar may provide relief. However, these should be used with caution and under medical advice.
When to Consider Treatment
Treatment is generally considered if the lesions are bothersome, become infected, or in cases where they spread extensively. Otherwise, the condition often resolves on its own.
Preventing Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is key to preventing the spread of molluscum contagiosum. Regular handwashing and not sharing personal items are effective preventative measures.
Avoiding Skin-to-Skin Contact
Encourage children to avoid direct contact with others who have the infection. In communal settings, ensure that shared items are disinfected regularly.
Tips for Parents and Caregivers
- Educate children on the importance of personal hygiene.
- Monitor and treat any skin conditions promptly.
- Consult a doctor if there are any concerns about the spread of the infection.
Living with Molluscum Contagiosum
Managing Symptoms at Home
Keep the affected areas clean and avoid scratching the lesions to prevent secondary infections. Using mild, unscented soaps and moisturizers can help soothe irritated skin.
Coping Strategies for Children
Children might feel self-conscious about visible skin lesions. Encouraging open communication and reassuring them about the temporary nature of the condition can be beneficial.
When to Seek Professional Help
Signs of Complications
Seek medical attention if lesions become red, swollen, or produce pus, as these could indicate an infection. Persistent or extensive lesions may require professional intervention.
Importance of Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor the condition and prevent complications. If using treatments, it is important to assess their effectiveness and adjust as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does molluscum contagiosum last in children?
The condition usually resolves on its own within 6 to 12 months, but it can last longer in some cases.
Can molluscum contagiosum be prevented?
Yes, by maintaining good hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated items.
Is molluscum contagiosum dangerous for children?
The condition is generally harmless but can be uncomfortable or aesthetically concerning.
What should I do if my child has molluscum contagiosum?
Monitor the lesions and consult a healthcare provider for advice on management and treatment.
Can molluscum contagiosum spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, the virus can spread through scratching or touching the lesions, so it's important to avoid these actions.
Are there any side effects of treatments for molluscum contagiosum?
Some treatments may cause skin irritation or temporary color changes. It's important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider.