Recognizing Malignant Melanoma in Children and Adults: Signs and Diagnosis
Guide on melanoma signs and diagnosis for all ages.
Introduction
Malignant melanoma is a severe form of skin cancer originating in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While it is less common than other skin cancers, melanoma is more dangerous due to its tendency to spread to other parts of the body if not detected early. Early detection and diagnosis can significantly improve prognosis and treatment outcomes, making it crucial for individuals to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melanoma.
What is Malignant Melanoma?
Malignant melanoma is categorized into several types, including superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and acral lentiginous melanoma. Each type has unique characteristics and growth patterns. According to recent statistics, melanoma accounts for a small percentage of skin cancer cases but causes the majority of skin cancer deaths. The prevalence of melanoma is increasing worldwide, emphasizing the need for public awareness and preventive measures.
Signs and Symptoms of Malignant Melanoma
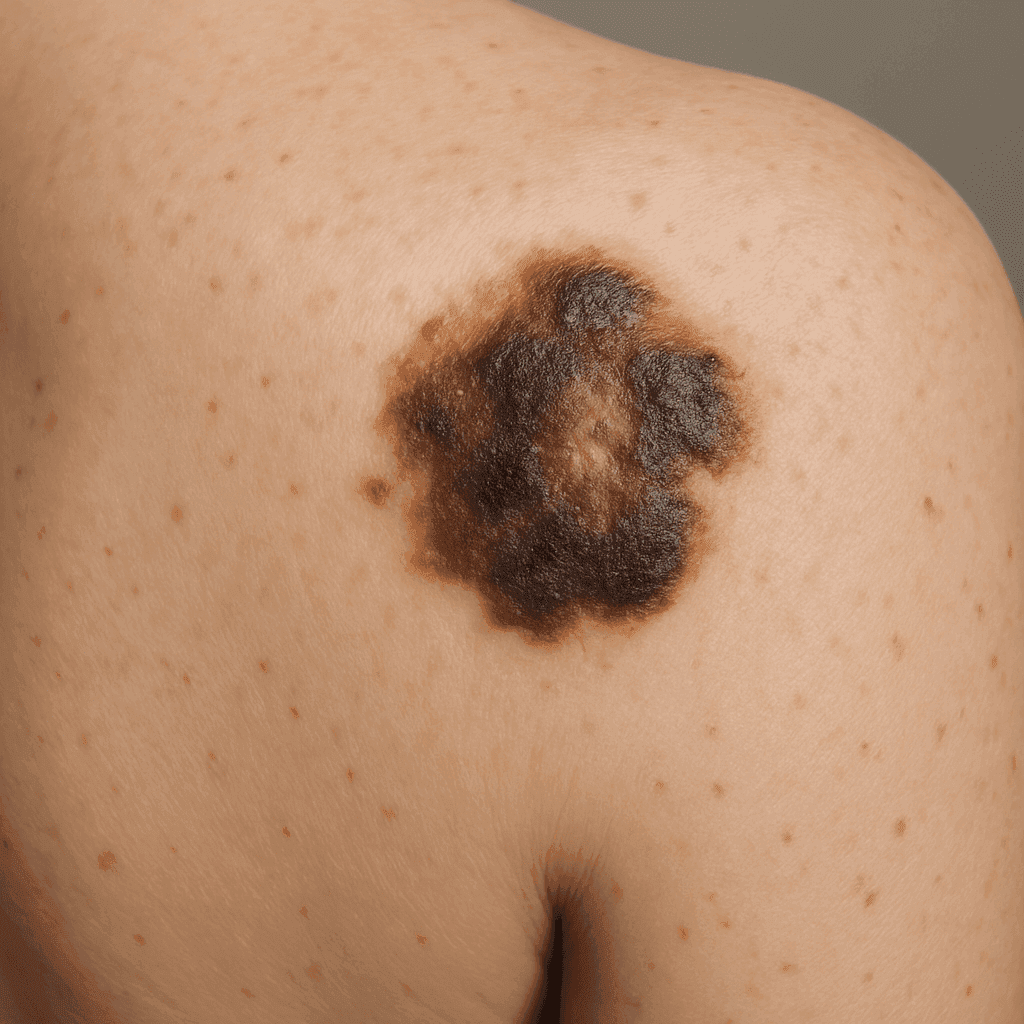
Common Signs in Adults
In adults, melanoma often presents as changes in existing moles, such as alterations in size, shape, or color. The appearance of new pigmented or unusual-looking growths on the skin can also be indicative of melanoma. It's essential to note changes in the skin's texture, as well as sensations like itching or tenderness.
Signs in Children
Pediatric melanoma can present differently than in adults. Children may develop amelanotic melanomas, which lack the typical pigmentation and may resemble benign skin conditions. Monitoring unusual skin changes, such as persistent lumps or non-healing sores, is vital in early detection.
Risk Factors for Malignant Melanoma
Genetic Factors
Family history plays a significant role in melanoma risk. Individuals with close relatives diagnosed with melanoma are at an increased risk. Inherited conditions such as dysplastic nevus syndrome can also predispose individuals to melanoma.
Environmental Factors
Ultraviolet (UV) exposure from sunlight or tanning beds is a primary environmental risk factor for melanoma. Lifestyle influences, such as spending significant time outdoors without sun protection, can further increase risk.
Diagnosis of Malignant Melanoma
Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination by a dermatologist is essential for diagnosing melanoma. This includes a visual inspection of the skin and the use of a dermatoscope, a handheld device that allows for a magnified view of skin lesions.
Biopsy Procedures
If a suspicious lesion is identified, a biopsy is performed to obtain a sample for histological examination. Types of biopsies include excisional, incisional, and punch biopsies. The procedure may vary depending on the lesion's size and location.
Differences in Diagnosing Melanoma in Children vs. Adults
Diagnosing melanoma in children presents unique challenges, as pediatric melanomas can mimic benign conditions. Pediatric dermatologists are skilled in identifying these subtle differences and employ specialized techniques for accurate diagnosis. Collaboration with a pediatric oncologist may be necessary for comprehensive care.
Preventive Measures and Regular Screenings
Implementing preventive measures, such as applying broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours, can reduce melanoma risk. Regular dermatological check-ups are crucial, especially for those with a family history or previous melanoma diagnosis. Early detection through routine screenings can lead to more effective treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, awareness and education are key components in the fight against malignant melanoma. By understanding the signs, symptoms, and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps in monitoring their skin health. Regular check-ups and preventive measures, coupled with advancements in technology, offer promising avenues for early detection and successful treatment of melanoma.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first signs of melanoma that I should watch for?
Typical early signs include changes in the size, shape, or color of moles. Any new growths or changes in existing moles should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How is melanoma diagnosed in children?
Diagnostic methods specific to pediatric cases often involve collaboration with pediatric dermatologists, who are trained to recognize the subtle differences in presentation.
Can melanoma be cured if caught early?
Early detection and treatment significantly improve the likelihood of curing melanoma, with many cases responding well to early intervention.
How often should I have my skin checked by a dermatologist?
It is generally recommended to have a professional skin evaluation annually, or more frequently if you have risk factors for melanoma.
Are there any non-invasive methods to detect melanoma?
Emerging technologies, such as AI-based skin photo analysis, offer non-invasive options for early melanoma detection, providing risk assessments that should be followed by a professional diagnosis.