Scabies: Symptoms and How to Prevent Infection
Understand scabies symptoms and prevention tips.
Introduction
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the infestation of the skin with the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. While it can affect anyone, understanding the symptoms and how to prevent infection is crucial for managing and controlling outbreaks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of scabies, focusing on symptoms, transmission, prevention, and treatment options.
What is Scabies?
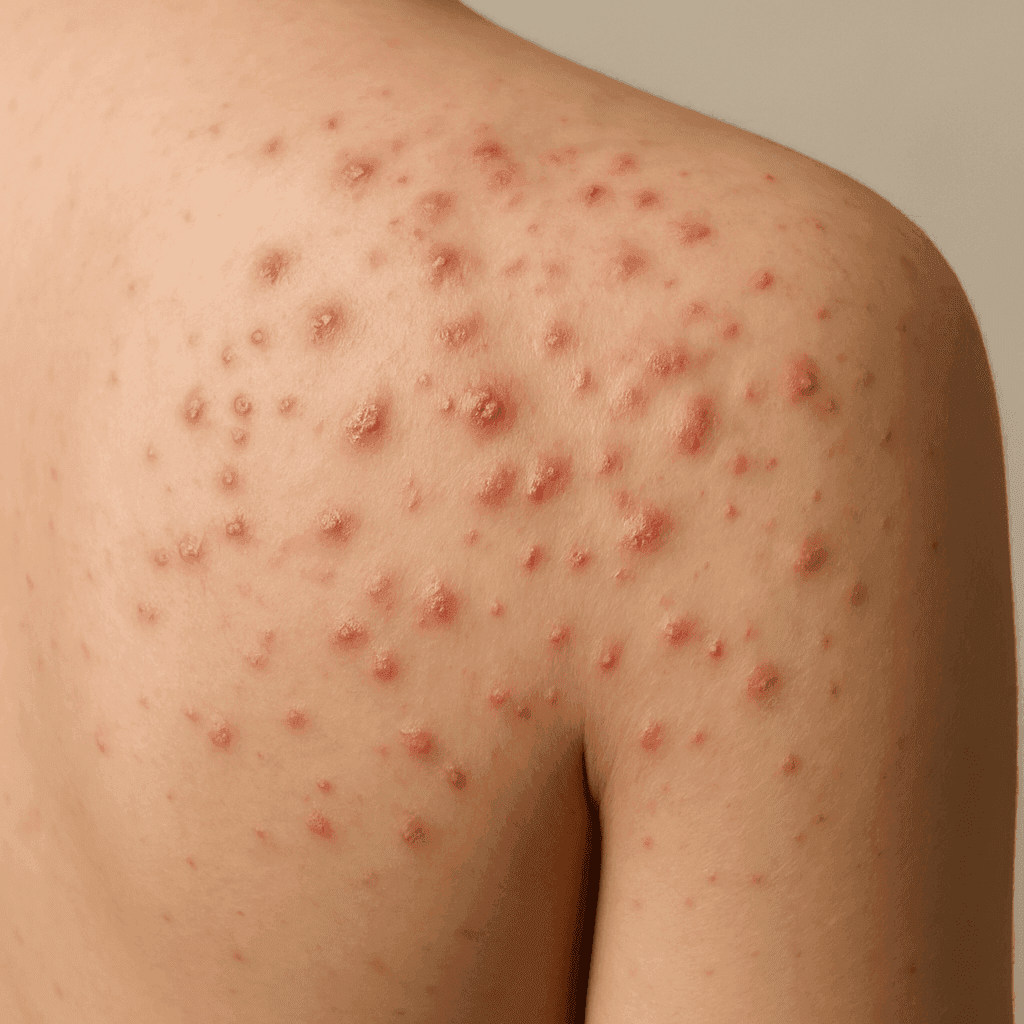
Scabies is an infestation that occurs when the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei burrows into the upper layer of the skin, causing intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The mites are too small to be seen with the naked eye, but their effects can be quite visible. Common risk factors include crowded living conditions, close physical contact, and compromised immune systems. It is important to note that scabies can spread rapidly in places like nursing homes, extended-care facilities, and child care centers.
Symptoms of Scabies
Early Signs to Watch For
The first signs of scabies often include intense itching, especially at night, and a rash that appears as small red bumps, blisters, or pustules. These are frequently found in folds of the skin, such as between the fingers, on the wrists, or around the elbows.
Common Symptoms in Adults
In adults, scabies typically presents as a widespread rash, often accompanied by severe itching. The rash can appear anywhere on the body but is most commonly found in the armpits, around the waist, and on the inner elbows.
Symptoms Specific to Children
Children may experience symptoms on different parts of the body, such as the face, neck, scalp, and soles of the feet. In infants, scabies can cause a more generalized rash that can be mistaken for other skin conditions, making diagnosis more challenging.
Differences Between Scabies and Other Skin Conditions
Scabies can be confused with eczema, dermatitis, or other allergic reactions. However, the presence of burrows—tiny, thread-like projections under the skin—is a distinctive sign of scabies.
How Scabies is Transmitted
Scabies is primarily spread through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infested person. It can also be transmitted indirectly through infested clothing or bedding, though this is less common. The contagious period of scabies extends until the mites and eggs are destroyed through treatment, making early intervention critical to prevent further spread.
Diagnosing Scabies
Diagnosing scabies typically involves a medical examination where a dermatologist may check for signs of mites, such as burrows, using a magnifying glass or dermatoscope. Sometimes, a skin scraping is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites or eggs. Early diagnosis is essential to begin treatment promptly and prevent spreading to others.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Prescription Medications
The primary treatment for scabies involves prescription medications such as permethrin cream or oral ivermectin, which kill the mites and their eggs. These treatments are usually applied to the entire body from the neck down and left on for a prescribed period.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
While over-the-counter treatments are available, they are generally not as effective as prescription medications. It is important to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist after treatment or if new symptoms develop, it is important to see a doctor for further evaluation and management. Persistent itching may require additional treatment, such as antihistamines or topical steroids.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Some popular home remedies for scabies include tea tree oil, neem oil, and aloe vera. While these remedies may help alleviate symptoms, their effectiveness in eradicating scabies mites is not well-documented. It is crucial to use home remedies as a complement to, not a replacement for, medical treatment. Always consult with a healthcare provider before trying new treatments to ensure safety and efficacy.
Preventing Scabies Infection
Tips to Avoid Contracting Scabies
To prevent scabies, avoid direct skin-to-skin contact with an infested person and refrain from sharing clothing, towels, or bedding. Regularly wash and dry these items using hot water and a hot dryer setting.
Preventing Spread in Households
If someone in your household is diagnosed with scabies, all members should receive treatment simultaneously to prevent reinfestation. It is also advisable to vacuum furniture and carpets thoroughly.
Hygiene Practices to Adopt
Maintaining good personal hygiene and keeping living spaces clean can reduce the risk of scabies. Regular handwashing and routine cleaning of commonly used surfaces are important preventive strategies.
Living with Scabies
Managing Symptoms at Home
Managing symptoms of scabies at home involves regular application of prescribed treatments and keeping the skin moisturized to reduce itching and irritation. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help manage itching, though they should only be used as directed.
Coping Strategies for Itching
Itching can be one of the most challenging symptoms of scabies. Applying cool compresses, soaking in a cool bath, or using calamine lotion can provide temporary relief. It's important to avoid scratching, which can lead to skin infections.
FAQ
What are the first signs of scabies?
The initial signs of scabies include intense itching, especially at night, and a rash that appears as small red bumps or blisters.
How can I prevent scabies from spreading in my home?
To prevent spreading, treat all household members simultaneously and wash all clothing and bedding in hot water.
Are there any effective home remedies for scabies?
While some home remedies like tea tree oil may help alleviate symptoms, they should not replace medical treatment.
How long does it take for scabies to clear up with treatment?
With proper treatment, scabies typically clears up in 1–2 weeks, though itching may persist for a few weeks longer.
Can scabies be mistaken for other skin conditions?
Yes, scabies can be mistaken for eczema or dermatitis due to similar symptoms like itching and rash.
Is it possible to get scabies from pets?
No, scabies is caused by a different mite in humans and is not transmitted by pets.