Skin Cancer and Sun Exposure: Myths and Facts
Explore myths and facts about sun exposure.
Introduction
Skin cancer is among the most common cancers worldwide, affecting millions annually. Understanding how sun exposure relates to skin cancer is crucial in taking preventive measures. Many myths surround sun exposure, creating confusion and misinformation. This article aims to clarify these myths with facts and provide practical advice for protecting skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Understanding Skin Cancer
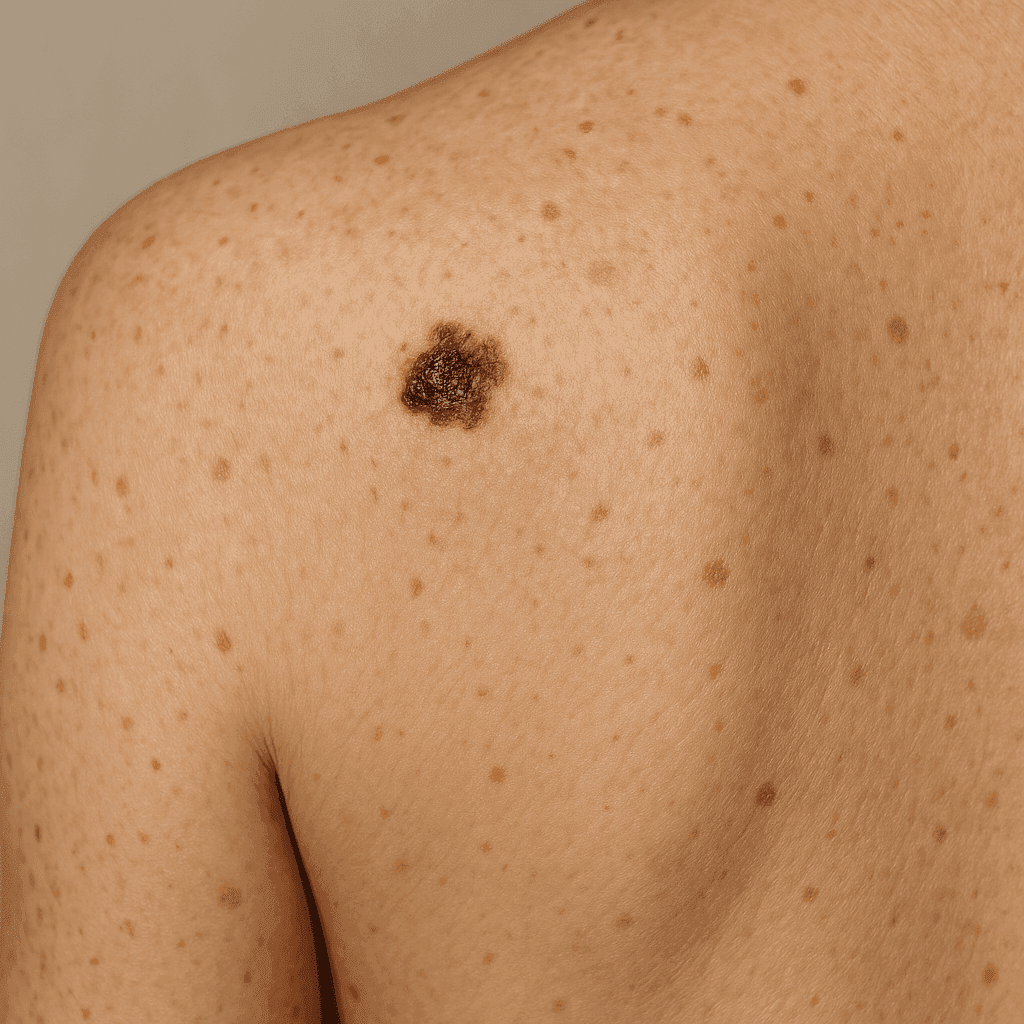
Skin cancer arises when there is uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. There are three main types: Basal Cell Carcinoma, the most common form, typically appearing as a pearly bump; Squamous Cell Carcinoma, which may look like a red scaly patch; and Melanoma, the deadliest form, often resembling a mole.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic factors play a role in skin cancer risk, but environmental factors, notably UV exposure, are significant contributors. Fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and excessive sun exposure increase risk. Personal habits, such as using tanning beds, also elevate risk.
The Role of Sun Exposure
Exposure to UV radiation is a leading cause of skin damage. UV rays penetrate the skin, causing changes that can lead to cancer. There are two main types of UV rays: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, contributing to aging and long-term damage, while UVB rays are primarily responsible for sunburn.
The Impact of Sun Exposure on Skin Health
Prolonged exposure to UV rays can cause the skin to lose elasticity, wrinkle, and become discolored. More importantly, it increases the risk of skin cancers. Protective measures, such as sunscreen and clothing, are essential to mitigate these risks.
Myths and Facts About Sun Exposure
Common Myths
There are several misconceptions about sun exposure. One is that sun exposure is always harmful, which isn't entirely true. Another myth is that only fair-skinned individuals are at risk for skin cancer, overlooking the fact that people of all skin tones are susceptible. Additionally, some believe tanning beds are a safer alternative to natural sunlight.
Debunking Myths with Facts
While excessive sun exposure can be harmful, moderate exposure is beneficial for vitamin D synthesis. Skin cancer can affect anyone, regardless of skin type. Tanning beds emit UV radiation similar to the sun, which can increase the risk of skin cancer.
Prevention and Protection
Effective Sun Protection Strategies
Protecting your skin from UV radiation involves several strategies. Sunscreen is crucial; apply it generously and reapply every two hours or after swimming. Protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses, offers additional defense. Seeking shade during peak sun hours reduces exposure.
Importance of Regular Skin Checks
Regular self-examinations and dermatologist visits are vital for early detection of skin changes. Early intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and a healthy lifestyle can further aid in prevention.
Early Detection and Treatment
Signs and Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Early signs of skin cancer include new moles, changes in existing moles, and sores that do not heal. Any suspicious changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Importance of Early Detection
Detecting skin cancer early increases the likelihood of successful treatment. Treatment options vary based on cancer type and stage, including surgical removal, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Early detection remains a critical component of effective management.
Conclusion
Understanding the myths and facts about sun exposure and skin cancer is essential for effective prevention and protection. By adopting safe sun practices and staying informed, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of skin cancer. Proactive management and regular skin checks are vital steps toward maintaining healthy skin.
FAQ
What are the first signs of skin cancer?
Look for new growths, unusual changes in moles, or persistent sores.
How often should I apply sunscreen?
Reapply every two hours and after swimming or sweating.
Can skin cancer be cured if detected early?
Yes, early detection increases treatment success.
Is it safe to get some sun exposure without protection?
Moderate exposure can be beneficial, but protection is crucial during peak hours.
Do darker-skinned individuals need to worry about skin cancer?
Yes, skin cancer can affect all skin types, though the risk varies.
How can I differentiate between a mole and skin cancer?
Changes in size, shape, color, or texture of a mole should be examined by a professional.