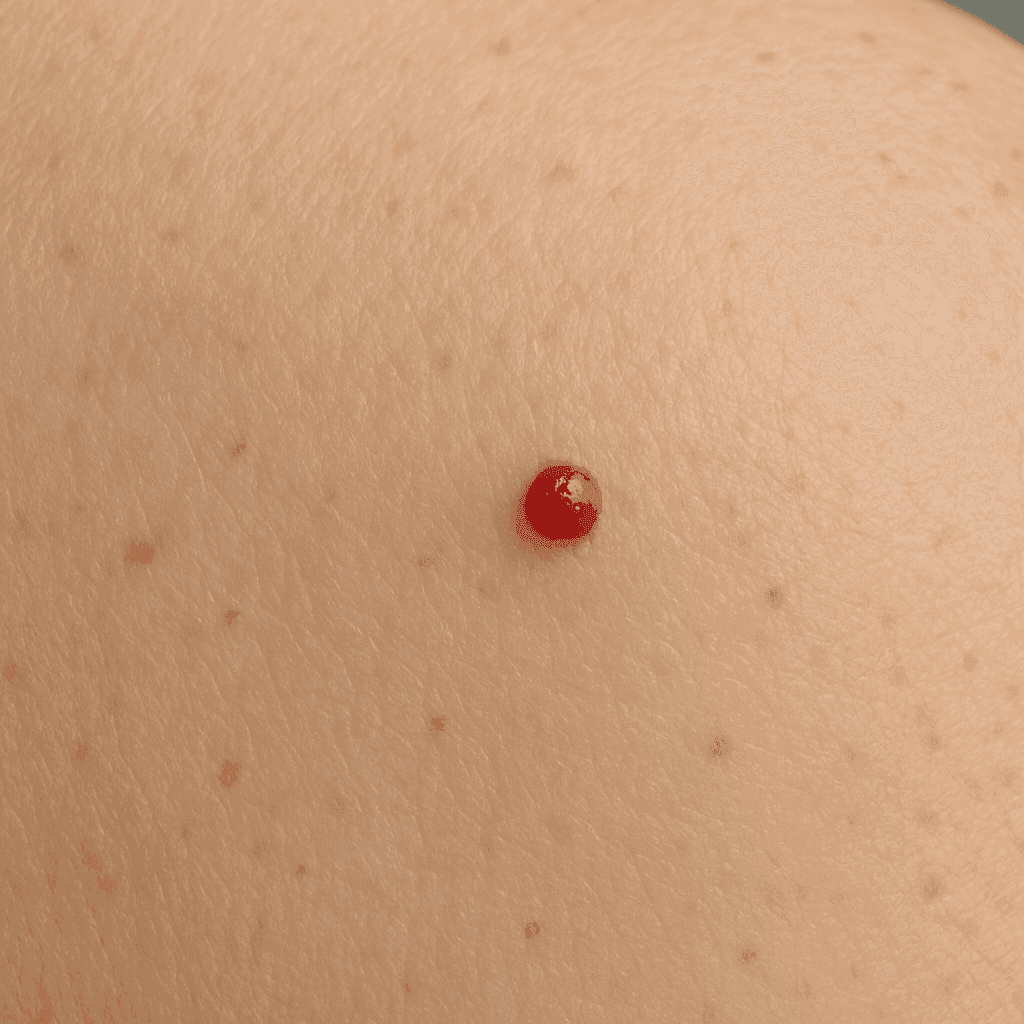
Vascular (Angioma / Cherry angioma).
Introduction
A vasculoma, also known as an angioma or cherry angioma, is a benign skin lesion resulting from the proliferation of blood vessels. Although not usually a health risk, they may be of interest for aesthetic or diagnostic reasons. Hemangiomas are common, especially among adults, and while they rarely require treatment, their presence can raise questions about skin health.
Types of hemangiomas
Cutaneous hemangioma
Cutaneous hemangioma is the most common type, appearing on the surface of the skin as small, red, raised spots. They can appear in various places on the body and often increase in size with age.
Choroidal angioma
Also known as cherry angioma, senile hemangioma occurs more often in older people. Its main feature is an intense red color, which results from the accumulation of small blood vessels.
Other types of hemangiomas
In addition to cutaneous and senile hemangiomas, there are other types, such as liver hemangiomas, which may require a different diagnostic and therapeutic approach.
Causes of hemangiomas
Genetic factors
Genetics plays an important role in the predisposition to the development of hemangiomas. They often occur familially, indicating a hereditary basis for these lesions.
Environmental influences
Exposure to UV radiation and certain chemicals can affect the development of hemangiomas, although their role is not clearly confirmed.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy or menopause, can affect the incidence of hemangiomas. Hormones can stimulate the development of new blood vessels in the skin.
Symptoms and diagnosis
How to recognize a hemangioma?
Hemangiomas are usually small, intensely red and slightly convex. They can be single or numerous and occur in various places on the body.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of hemangiomas is often based on their characteristic appearance. If in doubt, a dermatoscopy or skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Differences between hemangioma and other skin lesions
Hemangiomas can be confused with other lesions, such as moles. It is important to differentiate because some moles may require a different therapeutic approach.
Treatment of hemangiomas
When is treatment necessary?
Hemangiomas usually do not require treatment unless they cause aesthetic discomfort or bleeding. In such cases, it is worth consulting a dermatologist.
Treatment options
- Pharmacological: Rarely used, mainly for larger hemangiomas.
- Surgical: Surgical removal is possible, but most often unnecessary.
- Laser: Laser removal of hemangiomas is effective and often used for cosmetic purposes.
Natural treatment methods
Some people try natural methods, such as the use of essential oils, but their effectiveness is not scientifically proven.
Potential complications
Can hemangiomas be dangerous?
Hemangiomas are usually benign and pose no health risks. In rare cases, however, they can lead to complications such as bleeding or infection.
Risks associated with hemangiomas
Although hemangiomas rarely develop into malignant lesions, their presence can be mistaken for other potentially dangerous skin lesions. It is important to regularly monitor their appearance.
Prevention of hemangiomas
Can hemangiomas be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent hemangiomas, a healthy lifestyle and proper skin protection can limit their development.
The role of diet and lifestyle
A healthy diet rich in antioxidants can support overall skin health. Avoiding overexposure to the sun and using UV filters are also recommended.
Vascularity in children vs. adults
Differences in incidence and treatment
Hemangiomas in children are often temporary and disappear on their own. In adults, hemangiomas are more permanent and may require removal if they are a cosmetic problem.
When to see a doctor?
It is a good idea to consult a doctor if a hemangioma is rapidly changing, bleeding or causing other symptoms. Regular monitoring is key, especially if there are multiple lesions.
Summary
Hemangiomas are common, benign skin lesions that rarely require medical intervention. The key is to regularly monitor their appearance and, if in doubt, consult a dermatologist. Patients should be aware that although hemangiomas are usually harmless, any change in their appearance should be evaluated by a specialist.
FAQ
Can hemangiomas develop into cancer?
No, hemangiomas are benign lesions and do not transform into malignant tumors.
Is removal of a hemangioma painful?
Removal procedures, such as laser therapy, are usually minimally invasive and well tolerated by patients.
How often should hemangiomas be checked?
Regular follow-up, every few months, allows you to monitor any changes in the appearance of hemangiomas.