Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
Understand atopic dermatitis and safe treatment options.
Introduction
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflamed and itchy skin. It is one of the most common forms of eczema and affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment, as it can significantly impact one's quality of life. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for atopic dermatitis, while emphasizing the importance of a professional diagnosis.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
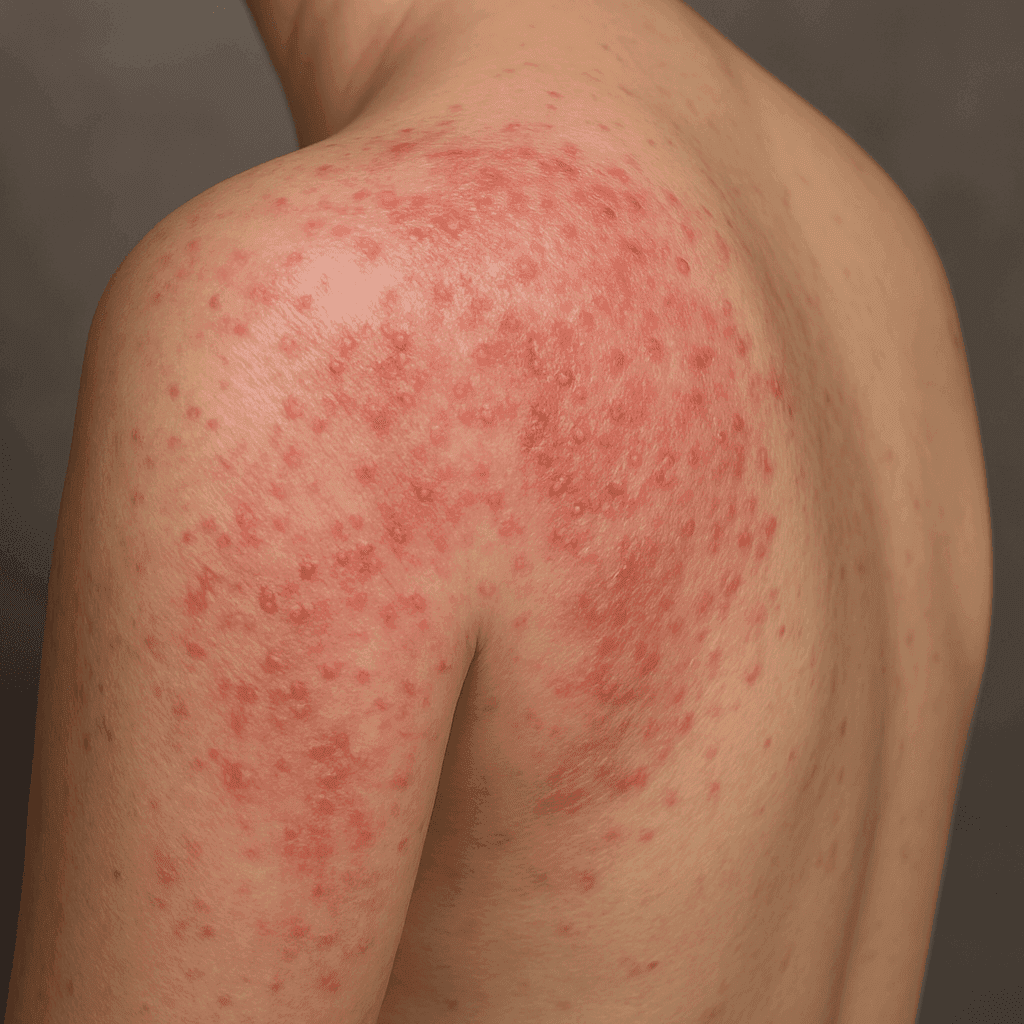
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that typically begins in childhood but can affect individuals at any age. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While often used interchangeably with eczema, atopic dermatitis is a specific type of eczema. Eczema is a general term that encompasses various inflammatory skin conditions, with atopic dermatitis being the most prevalent form. Understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of atopic dermatitis. Individuals with a family history of eczema, hay fever, or asthma are more likely to develop the condition. These genetic links suggest a hereditary component, making it a common trait among family members.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also trigger or exacerbate atopic dermatitis symptoms. Common triggers include exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. Additionally, irritants like harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics can worsen the condition. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is key to managing flare-ups effectively.
Immune System Involvement
Atopic dermatitis is associated with an overactive immune response. This heightened immune activity leads to inflammation and the characteristic symptoms of the condition. Understanding the immune system's role is essential for developing targeted treatments that can help manage the symptoms more effectively.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Common Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis symptoms can vary widely but often include dry, itchy skin, redness, and swelling. The condition is also characterized by the formation of blisters that may ooze and crust over. Over time, repeated scratching can lead to thickened skin, a condition known as lichenification.
Severity and Variations
The severity of symptoms can range from mild to severe and may fluctuate over time. Some individuals experience only minor irritation, while others may have more intense flare-ups. The severity often dictates the treatment approach, emphasizing the need for personalized care.
Age-Related Symptoms
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis can differ across age groups. In infants, the condition commonly appears on the face and scalp. In children and adults, it is more often found in the creases of the elbows, knees, and neck. Understanding these variations helps in tailoring treatment and management strategies.
Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination conducted by a dermatologist. During the examination, the doctor will assess the skin's appearance, focusing on the characteristic signs of atopic dermatitis.
Role of Allergy Testing
In some cases, allergy testing may be recommended to identify potential allergens that could be triggering symptoms. These tests can provide valuable insights into environmental or dietary factors contributing to flare-ups, allowing for more effective management of the condition.
Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment for atopic dermatitis due to their ability to reduce inflammation and itching. Calcineurin inhibitors are another option, particularly for sensitive areas like the face or groin, where steroids might cause side effects.
Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic treatments such as biologics and immunosuppressants may be prescribed. These medications target the immune system to reduce inflammation but require careful monitoring by a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, is another treatment option that can be effective for chronic atopic dermatitis. It involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision to reduce symptoms.
Natural and Home Remedies
Some individuals find relief through natural remedies, such as coconut oil, which can moisturize the skin, or oatmeal baths, which may soothe itching. While these remedies can be beneficial, it is crucial to discuss them with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your condition.
Managing Atopic Dermatitis
Daily Skin Care Routines
A consistent skin care routine is vital in managing atopic dermatitis. This includes using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to maintain skin hydration. It's also important to apply moisturizers immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Identifying triggers is a critical step in managing flare-ups. Keeping a diary to track potential triggers and flare-up occurrences can help pinpoint specific irritants or allergens. Once identified, these triggers should be avoided as much as possible.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Dietary changes, such as reducing the intake of known allergens, may help some individuals manage their symptoms. Additionally, stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation can be beneficial, as stress is a known trigger for many people with atopic dermatitis.
Atopic Dermatitis in Different Populations
Infants and Children
In infants and children, atopic dermatitis often presents as a rash on the cheeks, arms, and legs. Managing the condition in this age group requires gentle skin care products and regular application of emollients to prevent dryness.
Adults
Adults may experience atopic dermatitis differently, often with more localized patches of inflamed skin. Treatment in adults often involves a combination of topical treatments and lifestyle modifications to manage stress and environmental triggers.
Elderly
In the elderly, atopic dermatitis may present with more significant skin dryness and itching. The skin's natural barrier function diminishes with age, making regular moisturizing even more essential to prevent flare-ups.
Psychological Impact of Atopic Dermatitis
Mental Health Considerations
The chronic nature of atopic dermatitis can have a significant psychological impact, leading to issues such as anxiety and depression. The visible nature of the condition may also affect self-esteem and social interactions.
Coping Strategies and Support
Coping strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be beneficial. Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and strategies, offering comfort and advice from others who understand the challenges of living with atopic dermatitis.
Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis
Tips to Prevent Flare-Ups
Preventing flare-ups involves maintaining a consistent skin care routine and avoiding known triggers. Regular use of moisturizers and protective clothing can help minimize exposure to irritants.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Long-term management of atopic dermatitis requires a multi-faceted approach, including medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and regular consultations with a dermatologist. Keeping abreast of new treatment options and strategies is also essential for effective management.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between atopic dermatitis and eczema?
While atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema, eczema is a broader term that includes various skin conditions characterized by inflammation and itchiness. Atopic dermatitis is the most common form, often linked to genetic and environmental factors.
Can diet affect atopic dermatitis?
Diet can influence atopic dermatitis symptoms, especially if specific food allergies are present. Identifying and avoiding these allergens can help manage symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist is recommended.
Are there any natural remedies for atopic dermatitis?
Natural remedies such as coconut oil and oatmeal baths can provide relief for some individuals. However, it's important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure they're safe and effective for your specific case.
How can I prevent atopic dermatitis flare-ups?
Preventing flare-ups involves a consistent skincare routine, identifying and avoiding triggers, and managing stress. Regular moisturizing and protective measures against environmental irritants can also help.
Is atopic dermatitis contagious?
No, atopic dermatitis is not contagious. It is an inflammatory skin condition that results from genetic and environmental factors, not from an infectious agent.
What should I do during a severe flare-up?
During a severe flare-up, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment options, which may include topical or systemic medications. Keeping the skin moisturized and avoiding known irritants can also aid in managing symptoms.