Tinea
Symptoms, treatment and prevention of dermatophytosis.
Introduction
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea, is a common infection caused by dermatophyte fungi. It occurs in both children and adults, affecting different areas of the body such as the feet, groin and scalp. Due to its easy spread and recurrent nature, ringworm is a significant health problem in the population. Understanding its causes, symptoms and effective treatments is key to the effective management of this disease.
Causes of dermatophytosis
Dermatomycosis is caused by fungi that thrive in warm and moist conditions. Risk factors include frequent use of public swimming pools, wearing tight shoes and neglecting personal hygiene. Infection usually occurs through direct contact with infected people, animals or surfaces.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing dermatophytosis:
- Excessive sweating
- Wearing impermeable clothing
- Reduced immunity
- Frequent use of saunas and swimming pools
Symptoms of dermatomycosis
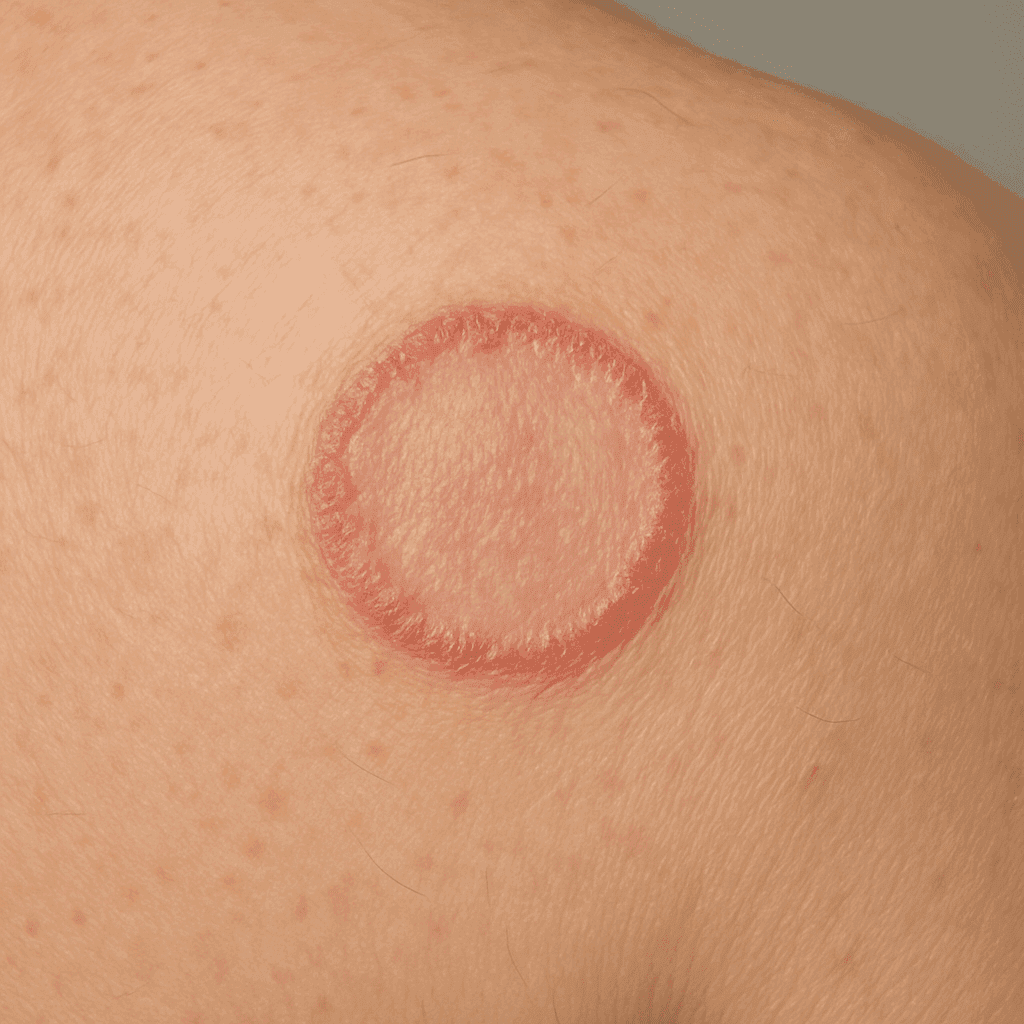
The symptoms of dermatomycosis can vary depending on the site of infection and the age of the patient. Generally they include itching, redness, scaling of the skin and the appearance of characteristic ring-shaped lesions.
How to recognise the infection
In children, symptoms may be more severe and skin lesions may cover larger areas. In adults, the infection is often limited to smaller, localised lesions that may be more difficult to see without close inspection.
Diagnosis
Successful diagnosis of dermatophytosis is mainly based on clinical and laboratory investigations. The dermatologist may order microscopic examination of skin scrapings or cultures to confirm the presence of fungi.
Methods of diagnosis
- Clinical examination
- Microscopy
- Fungal culture
Treatment of dermatophytosis
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment is the most effective way to treat dermatophytosis. Antifungal drugs, such as terbinafine or clotrimazole, are available as creams or tablets. Dosage and duration of treatment depend on the site and intensity of the infection.
Home treatment
Some patients choose to support pharmacotherapy with home methods. Natural remedies, such as the use of tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar, can support treatment, but their effectiveness is limited.
Prevention of dermatophytosis
Prevention of dermatophytosis is based on maintaining good personal hygiene and taking precautions in public places. Wearing airy clothing and changing underwear regularly is important.
Dermatomycosis and diet
Diet plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of dermatophytosis. Eating foods rich in probiotics can support the immune system, and avoiding excess simple sugars can limit fungal growth.
Dermatomycosis in animals
Dermatophytosis not only affects humans, but also pets. Symptoms in animals include hair loss and reddening of the skin. Treatment requires consultation with a vet and the use of specialised preparations.
Summary
Dermatophytosis is a common infection that can be effectively prevented and treated through good hygiene, pharmacotherapy and changes in eating habits. It is a good idea to consult your doctor if you have worrying symptoms.
FAQ
Is dermatophytosis contagious?
Yes, dermatophytosis is contagious and can be transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or infected objects.
How long does it take to treat dermatophytosis?
Treatment time depends on the location and severity of the infection, and usually takes from a few weeks to a few months.
References
- Scientific articles on dermatophytes
- Dermatology textbooks
- Clinical studies on the efficacy of antifungal drugs
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing dermatophytosis:
- Excessive sweating
- Wearing of impermeable clothing
- Reduced immunity
- Frequent use of saunas and swimming pools
Symptoms of dermatomycosis
The symptoms of dermatomycosis can vary depending on the site of infection and the age of the patient. Generally, they include itching, redness, scaling of the skin and the appearance of characteristic annular lesions.
How to recognise the infection
In children, symptoms may be more severe and skin lesions may cover larger areas. In adults, the infection is often limited to smaller, localised lesions that may be more difficult to see without close inspection.
Diagnosis
Successful diagnosis of dermatophytosis is mainly based on clinical and laboratory investigations. The dermatologist may order microscopic examination of skin scrapings or cultures to confirm the presence of fungi.
Methods of diagnosis
- Clinical examination
- Microscopy
- Fungal culture
Treatment of dermatophytosis
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment is the most effective treatment for dermatophytosis. Antifungal drugs, such as terbinafine or clotrimazole, are available as creams or tablets. Dosage and duration of treatment depend on the site and intensity of the infection.
Home treatment
Some patients choose to support pharmacotherapy with home methods. Natural remedies, such as the use of tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar, can support treatment, but their effectiveness is limited.
Prevention of dermatophytosis
Prevention of dermatophytosis is based on maintaining good personal hygiene and taking precautions in public places. Wearing airy clothing and changing underwear regularly is important.
Dermatomycosis and diet
Diet plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of dermatophytosis. Eating probiotic-rich foods can support the immune system, and avoiding excess simple sugars can limit fungal growth.
Dermatomycosis in animals
Dermatophytosis not only affects humans, but also pets. Symptoms in animals include hair loss and reddening of the skin. Treatment requires consultation with a vet and the use of specialised preparations.
Summary
Dermatophytosis is a common infection that can be effectively prevented and treated through good hygiene, pharmacotherapy and changes in eating habits. It is a good idea to consult your doctor if you have worrying symptoms.
FAQ
Is dermatophytosis contagious?
Yes, dermatophytosis is contagious and can be transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or infected objects.
How long does it take to treat dermatophytosis?
Treatment time depends on the location and severity of the infection, and usually takes from a few weeks to a few months.
References
- Scientific articles on dermatophytes
- Dermatology textbooks
- Clinical studies on the efficacy of antifungal drugs