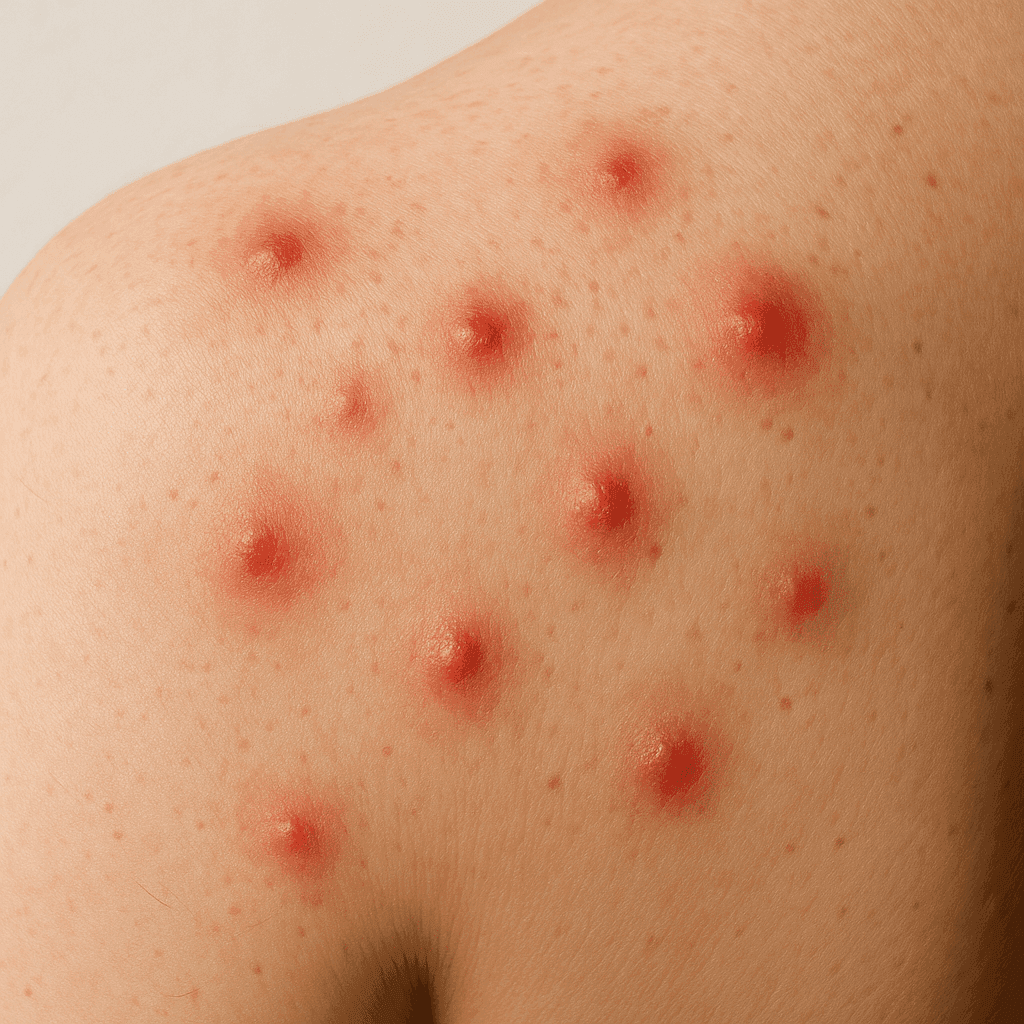
Insect bites
A guide to the diagnosis and treatment of insect bites.
Introduction
Insect bites are a common problem that most people encounter during their lifetime. Although they may seem trivial, in some cases they lead to serious allergic reactions or skin infections. Understanding the different types of bites and how to treat them is key to maintaining skin health and overall wellbeing. From minor irritations to potential health risks, knowing the symptoms and management methods can greatly improve quality of life.
Types of insect bites
Mosquito bites
Mosquitoes are one of the most common biting insects. Their bites are often easily recognisable by their characteristic red swelling and itching. In some people, reactions can be more severe, leading to large blisters and intense itching. Cold compresses and topical soothing gels are useful to alleviate these symptoms.
Bee and wasp stings
Bee and wasp stings can be painful and lead to swelling. A characteristic symptom is pain at the site of the sting, which can be intense. In the event of a sting, the stinger should be removed if visible and a cold compress applied to reduce swelling. In case of allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, immediate medical attention is required.
Tick bites
Ticks can be difficult to spot on the skin, but their bites can lead to serious diseases such as Lyme disease. Removal of the tick should be done as soon as possible, using tweezers, grasping it as close to the skin as possible and pulling gently. Once the tick has been removed, the bite site should be thoroughly cleaned and observed for signs of infection.
Bites from fleas and lice
Fleas and lice are a common problem among children and pets. Flea bites often appear in clusters and can cause severe itching. Treatment includes the use of specialised shampoos and insecticides, and keeping the home clean to prevent recurrence.
Symptoms and reactions to insect bites
Typical symptoms of insect bites include redness, swelling and itching. In some cases, more serious reactions such as hives or anaphylaxis can occur, which require immediate medical intervention. Allergic reactions are characterised by swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat and difficulty breathing and can be life-threatening. People with a history of allergies should be particularly careful and always carry antihistamines or adrenaline.
Treatment and alleviation of the symptoms of bites
Home remedies
Natural methods to relieve insect bite symptoms include the use of aloe vera, tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar. These remedies can help reduce itching and swelling. Additionally, cold compresses can provide relief from intense itching.
Pharmacological treatment
Various creams and ointments are available that can be applied topically to the bite to relieve symptoms. Antihistamines can be helpful for more severe allergic reactions. It is important to use the medication as prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist.
Prevention of insect bites
Prevention of insect bites includes the use of personal protective measures, such as wearing long sleeves and trousers, especially in areas with high insect numbers. Insect repellents that can be applied to the skin and clothing are also effective. It is also a good idea to avoid areas where insects can breed, such as standing water and dense bushes.
Complications associated with insect bites
Although most insect bites are harmless, they can lead to skin infections, especially if scratched persistently. The bite site should be observed for signs of infection, such as redness, pain, warmth and pus discharge. Some insects can also transmit diseases, such as Lyme disease and malaria, highlighting the importance of prevention.
When to see a doctor
It is a good idea to see a doctor if the bite symptoms persist or worsen, if systemic symptoms such as fever appear, or if an allergic reaction is suspected. Prompt medical intervention is crucial in cases of severe allergic reactions.
Summary
Insect bites are a problem that can be effectively controlled with proper knowledge and preventive measures. Knowledge of symptoms, potential complications and treatment methods is key to maintaining health and comfort. Prevention, combined with education, can significantly minimise the risk of bites and their associated complications.