Seborrhoeic dermatitis
Causes, symptoms and treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis.
Introduction
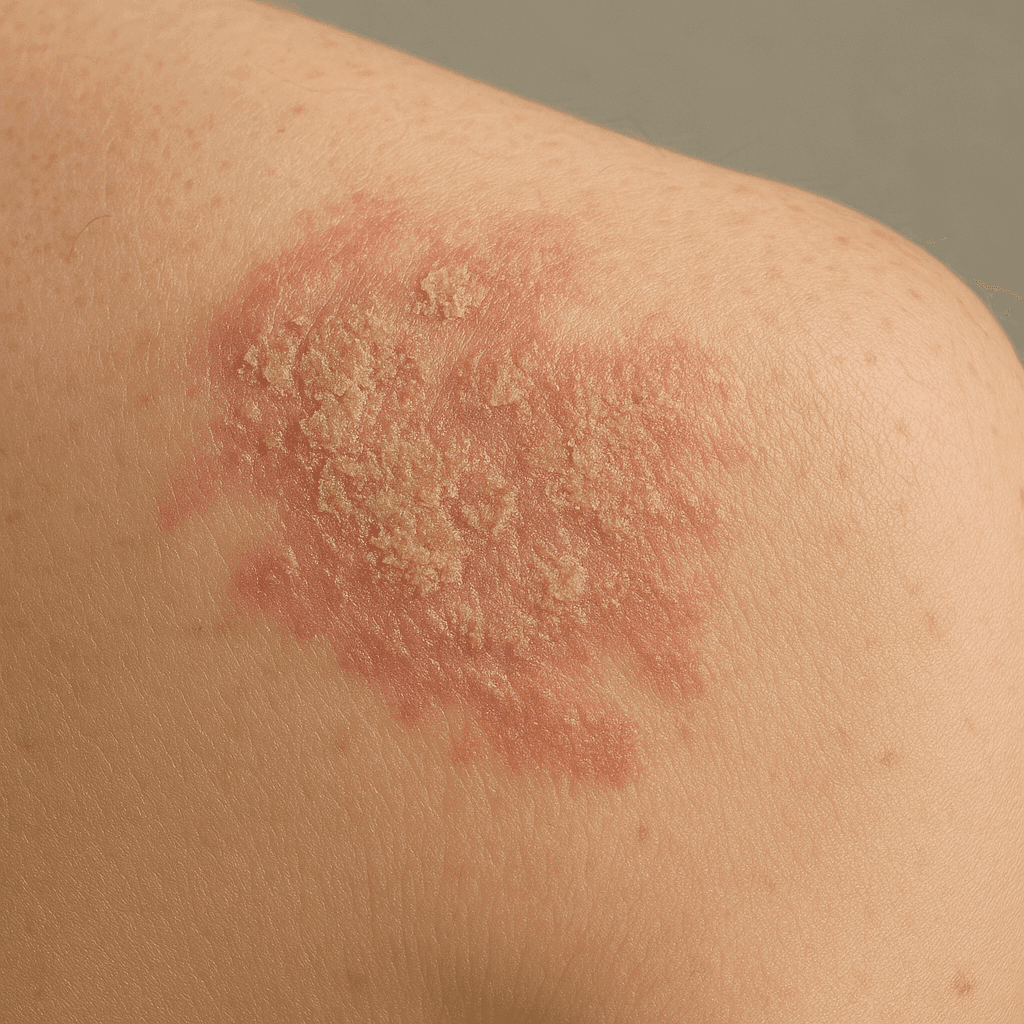
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a chronic dermatological disease characterised primarily by red, scaly and pruritic skin. It often occurs in areas with abundant sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, chest and back. The condition can affect both infants and adults, with symptoms varying according to age group.
Causes of seborrhoeic dermatitis
Genetic factors
Seborrhoeic dermatitis often runs in families, suggesting that genetics play an important role in its development. Individuals with families with a history of skin disease may be more likely to develop the condition.
Impact of hormones
Hormones, particularly androgens, can affect the activity of the sebaceous glands, which in turn can contribute to the symptoms of seborrhoeic dermatitis. For this reason, the condition often increases during periods of hormonal change, such as puberty or menopause.
The role of Malassezia yeasts
Malassezia yeasts are part of the natural microflora of the skin, but their excessive proliferation can lead to inflammation. It is thought that these bacteria may play a key role in the pathogenesis of seborrhoeic dermatitis.
Symptoms of seborrhoeic dermatitis
Characteristic skin lesions include redness, itching and scaly skin. In infants, it often presents in the form of parched skin on the scalp, whereas in adults, symptoms may be more extensive and also involve the face or chest.
Differences in symptoms between infants and adults
In infants, seborrhoeic dermatitis most often manifests as scaly, yellowish lesions on the scalp. In adults, on the other hand, the lesions may cover more extensive areas of the body and the symptoms may be more troublesome, often associated with intense itching.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of seborrhoeic dermatitis is usually based on clinical assessment. The dermatologist can diagnose the disease on the basis of characteristic symptoms and medical history. Sometimes it may be necessary to differentiate with other diseases, such as psoriasis or atopic dermatitis, which may show similar symptoms.
Treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment often includes the use of steroid creams and ointments to help reduce inflammation and pruritus. Antifungal drugs can also be effective in treatment, especially if Malassezia yeast is involved in the development of the disease.
Natural and home treatments
Many people seek natural ways to alleviate symptoms, such as using herbs (such as aloe vera) or dietary supplements to support skin health. Dietary changes, such as limiting the intake of simple sugars or saturated fats, can also be beneficial.
Skin care
Choosing the right cosmetics is crucial for people with seborrhoeic dermatitis. Products should be mild, non-comedogenic and contain no irritants. Regular hygiene and avoidance of alcohol-based cosmetics can help manage symptoms.
Preventing recurrences
Preventing recurrence of seborrhoeic dermatitis requires lifestyle changes. Regular stress management, a healthy diet and proper skin care can help to keep the condition under control.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis and other conditions
Differences between seborrhoeic dermatitis and psoriasis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis and psoriasis share several common features, but differ in pathogenesis and symptoms. Psoriasis is often characterised by thick, silvery scales and may involve the nails and joints.
Relationship to other dermatological diseases
Seborrhoeic dermatitis may coexist with other dermatological diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
Summary
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a chronic condition that requires regular follow-up and management. It is crucial to understand the causes and symptoms in order to manage the condition effectively. Patients should pay attention to lifestyle, skin care and avoid triggers.
FAQ
Is seborrhoeic dermatitis contagious?
No, seborrhoeic dermatitis is not contagious. It is a chronic skin condition linked to genetic and environmental factors.
What are the best shampoos for seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Shampoos containing antifungal ingredients, such as ketoconazole, and mild cleansers can help control symptoms on the scalp.