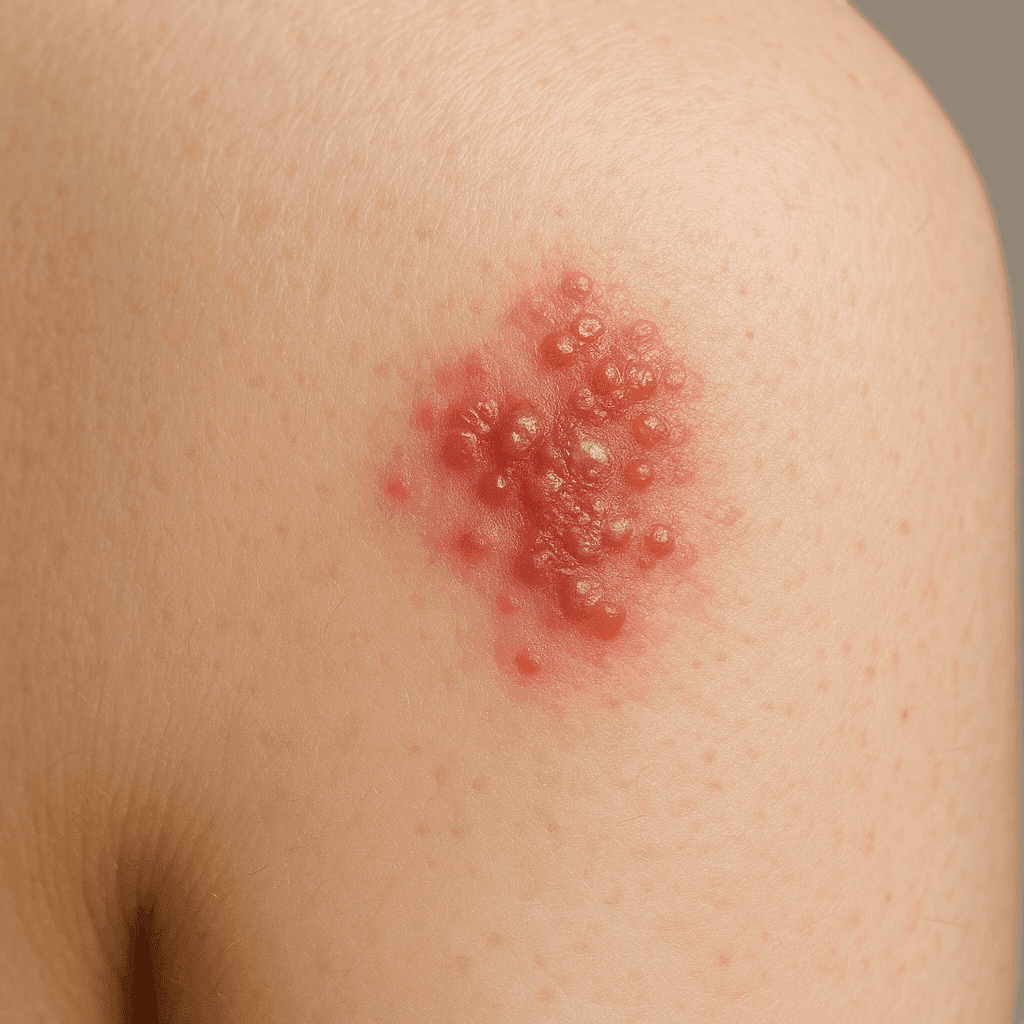
Herpes labialis (Herpes Simplex)
Symptoms, treatment and prevention of herpes labialis.
What is herpes labialis?
Herpes labialis, also known as herpes simplex, is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is a common infection that most commonly manifests as painful blisters around the mouth. The virus can come in two types: HSV-1, which is most often responsible for labial lesions, and HSV-2, mainly associated with genital herpes.
Definition and aetiology
Herpes Simplex Virus is a DNA virus of the Herpesviridae family. After primary infection, the virus remains latent in the body and can be reactivated when exposed to various factors such as stress, infections or sun exposure. The HSV-1 type is best known for causing herpes labialis, while HSV-2 predominantly causes genital herpes.
Epidemiology
Herpes labialis is one of the most common viral infections worldwide. It is estimated that most adults may have been exposed to HSV-1. The infection affects people of all ages, but those with weakened immune systems and children and adolescents, who may come into more frequent contact with carriers of the virus, are most at risk.
Symptoms of herpes labialis
Early symptoms
The first signs of herpes labialis may include tingling, itching or burning around the mouth. These prodromal symptoms are often a harbinger of the appearance of blisters. Early recognition of these symptoms may allow faster initiation of drug treatment, which can shorten the duration of the infection.
Advanced symptoms
As the infection progresses, characteristic painful blisters appear, which may cluster into larger lesions. These blisters usually rupture, forming painful sores that scab over time. The duration of a full-blown herpes episode is usually seven to 10 days, although this can vary depending on the individual's response to the infection.
Causes and risk factors
Causes of recurrences
Recurrences of herpes labialis can be triggered by various factors, such as emotional stress, fatigue, illnesses that weaken the immune system, and exposure to intense UV radiation. Recurrences may be more frequent in people who have a weakened immune system due to chronic diseases or the use of immunosuppressive drugs.
Risk factors
The risk of contracting herpes labialis is increased if there is close contact with an infected person, which facilitates transmission of the virus. In addition, people with frequent respiratory infections, which can weaken the body, are more susceptible to a viral reaction in the form of herpes.
Diagnosis of herpes labialis
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of herpes labialis is mainly based on clinical assessment, i.e. the recognition of characteristic skin lesions. In doubtful cases or to confirm the diagnosis, doctors may order laboratory tests such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or serological tests that detect the presence of antibodies to the HSV virus.
Treatment of herpes labialis
Pharmacotherapy
The most commonly used drugs to treat herpes labialis are acyclovir, valacyclovir and famcyclovir. These antiviral agents can shorten the duration of symptoms and reduce the severity of the infection. It is important to start therapy as early as possible, preferably when the first prodromal symptoms appear.
Home treatment
Home remedies to alleviate herpes labialis symptoms include the use of cold compresses, which can reduce pain and swelling. Avoiding irritating lip products and using moisturising lotions with UV filters are also recommended.
Natural treatment
Some herbs, such as lemon balm, have antiviral properties and can help treat herpes. Supplements, such as lysine, may also help reduce the frequency of recurrences, although their effectiveness has not been conclusively proven in clinical trials.
Prevention of herpes labialis
Prevention
Prevention of herpes labialis recurrence includes avoiding triggers, such as excessive sun exposure, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Those prone to recurrence should use lip balms with a high UV filter and avoid stress and exhaustion.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular physical activity and adequate rest can support the immune system and reduce the risk of herpes recurrence.
Herpes labialis and quality of life
Impact on daily functioning
Herpes labialis can significantly affect quality of life, causing physical and psychological discomfort. The skin lesions can be painful and their visibility is often associated with feelings of shame and lowered self-esteem, which can affect personal and professional life.
Coping with herpes
Strategies for coping with herpes include accepting the disease and educating oneself about the condition to better control the situation. Psychological support and talking to people who are experiencing similar problems can also help to cope with the emotional effects of the infection.
Summary
Key findings
Herpes labialis is a common viral infection that can recur due to a variety of factors. Early recognition of symptoms and appropriate treatment can shorten the duration of the infection and reduce its severity. There are effective pharmacological treatments as well as home and natural remedies to support the therapy.
Recommendations
To minimise the risk of recurrence of herpes labialis, it is recommended to take care of the immune system through a healthy lifestyle, avoiding stress and using adequate sun protection. In case of frequent recurrences, it is advisable to consult your doctor for a personalised prevention and treatment plan.