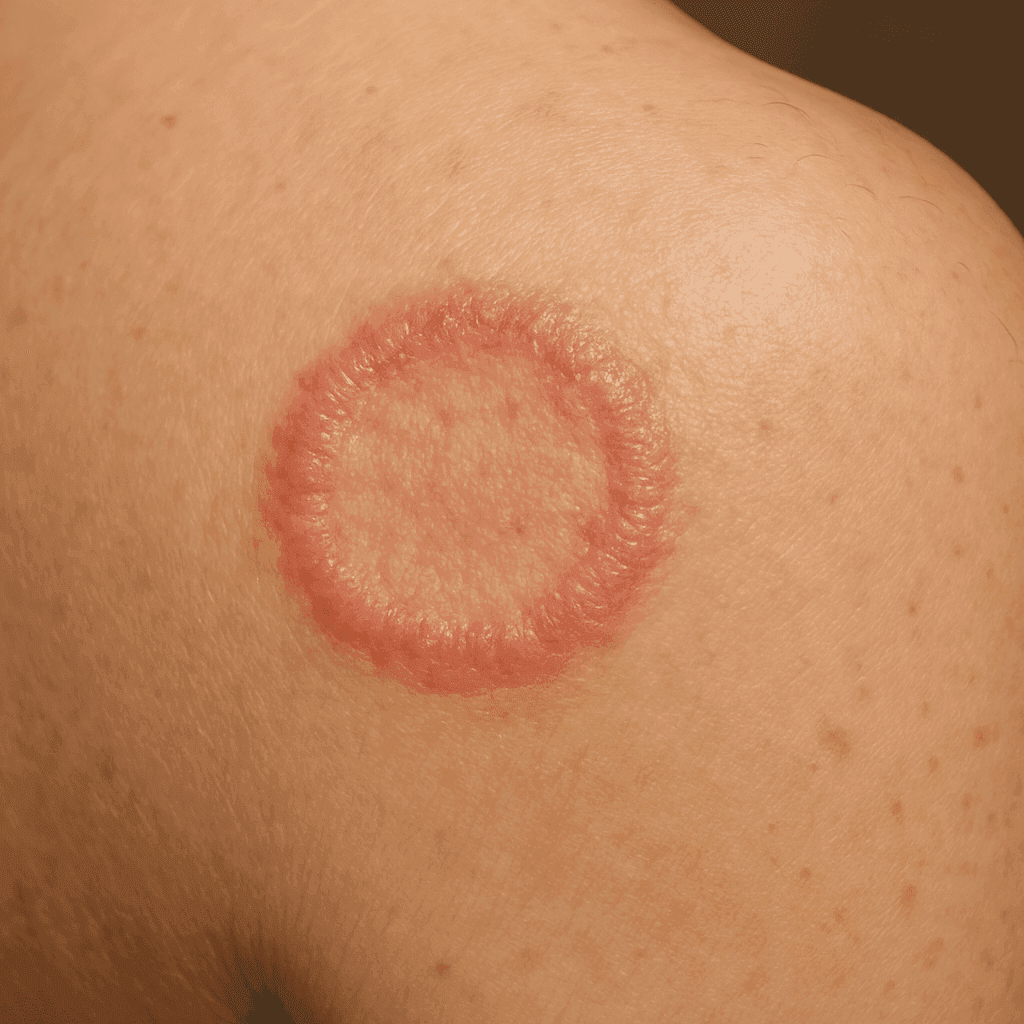
Skin candidiasis (Tinea Corporis)
Learn about the causes, symptoms and treatment of skin candidiasis.
What is cutaneous candidiasis?
Cutaneous candidiasis, also known as cutaneous candidiasis, is an infection caused by yeasts of the genus Candida. It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages, both adults and children. Cutaneous candidiasis usually manifests itself in moist and warm areas such as skin folds, under the breasts, in the groin or between the toes. These fungi naturally occur in our body, but under certain conditions they can multiply excessively, leading to infection.
Symptoms of skin candidiasis
How can you recognise skin candidiasis?
The symptoms of skin candidiasis can vary, but most commonly include redness, itching, burning and scaling of the skin. In some cases, blisters and oozing lesions may also appear. Characteristically, skin lesions often occur in moist and warm areas.
Differences between candidiasis and other skin infections
Candidiasis is often confused with other skin infections, such as dermatophytosis or psoriasis. The difference, however, is the location and type of lesions. Dermatophytic mycoses often occur on the feet and hands, whereas candidiasis occurs in the skin folds. Psoriasis is characterised by silvery scales, which distinguishes it from candidiasis.
Causes and risk factors
Risk factors for cutaneous candidiasis
The most common risk factors for cutaneous candidiasis include a humid environment, excessive sweating, obesity, diabetes, and long-term use of antibiotics or corticosteroids. People with a weakened immune system are also more likely to develop this infection.
Effect of stress on the development of skin candidiasis
Stress, as a factor that weakens the immune system, can contribute to the development of skin candidiasis. Long-term stress leads to an increase in cortisol levels, which can disrupt the balance of the skin microflora and promote yeast infections.
Skin candidiasis and diabetes
People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing skin candidiasis, as blood glucose levels are a factor that encourages the growth of candida. High sugar levels create an ideal environment for fungal growth, so people with diabetes should take special care with their skin hygiene.
Skin candidosis diagnosis
The diagnosis of skin candidiasis is mainly based on a thorough clinical examination and medical history. The dermatologist may order a microscopic examination or a fungal culture to confirm the presence of Candida yeasts. In some cases, additional laboratory tests may be necessary to exclude other skin conditions or infections.
Treatment of cutaneous candidiasis
Effective treatments for cutaneous candidiasis
Treatment of cutaneous candidiasis most commonly involves the use of topical antifungal preparations such as creams containing clotrimazole, miconazole or econazole. For more severe infections, the doctor may prescribe oral antifungal drugs such as fluconazole.
Treatment of skin candidiasis with natural methods
Natural methods of treating skin candidiasis include the use of tea tree oil, garlic and apple cider vinegar, which have antifungal properties. However, it is worth remembering that natural methods should be used as an adjunct to drug therapy, not as a replacement for it.
Home remedies for skin candidiasis
Epsom salt baths can be used at home to alleviate the symptoms of candidiasis. It is also important to keep the skin dry and avoid wearing tight clothing, which promotes the development of infection.
How long does it take to treat skin candidiasis?
The duration of treatment for skin candidiasis depends on the severity of the infection. Typically, topical treatment lasts from a few days to two weeks, while for more severe infections oral medication may be used for several weeks.
Prevention of skin candidiasis
Dietary support for the treatment of candidiasis
A diet rich in vegetables, healthy fats and protein, and low in simple sugars and processed foods, can support the treatment of skin candidiasis. It is also worth including probiotics in the diet to help balance the intestinal microflora.
Preventing skin candidiasis
To prevent skin candidiasis, maintain personal hygiene, keep skin dry and avoid wearing tight, unventilated clothing. Regular hand washing and the use of antibacterial soaps can also help prevent infection.
Cutaneous candidiasis in children
Cutaneous candidiasis can also affect children, especially newborns and infants. Symptoms in children are similar to those in adults, but may be more severe due to the delicacy of the child's skin. It is important that parents pay attention to any skin lesions and consult their paediatrician if an infection is suspected.
When to go to the doctor?
It is advisable to consult a doctor if the symptoms of skin candidiasis do not disappear despite home treatment or if the infection is recurrent. The doctor may recommend additional tests and tailor the treatment to the individual patient.
Summary
Cutaneous candidiasis is a common infection that can occur in a variety of circumstances. Proper diagnosis and treatment is key to prevent recurrence and complications. Proper hygiene, diet and control of risk factors can significantly reduce the risk of contracting the disease.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Is cutaneous candidiasis contagious?
Cutaneous candidiasis is not considered to be very contagious, but it can be transmitted in moist conditions with direct contact.
What are the most common mistakes in the treatment of cutaneous candidiasis?
The most common mistakes are stopping treatment too early and using inappropriate preparations, which can lead to recurrence.
Can cutaneous candidiasis recur?
Yes, skin candidiasis can recur, especially if risk factors are not eliminated or treatment is not carried out correctly.