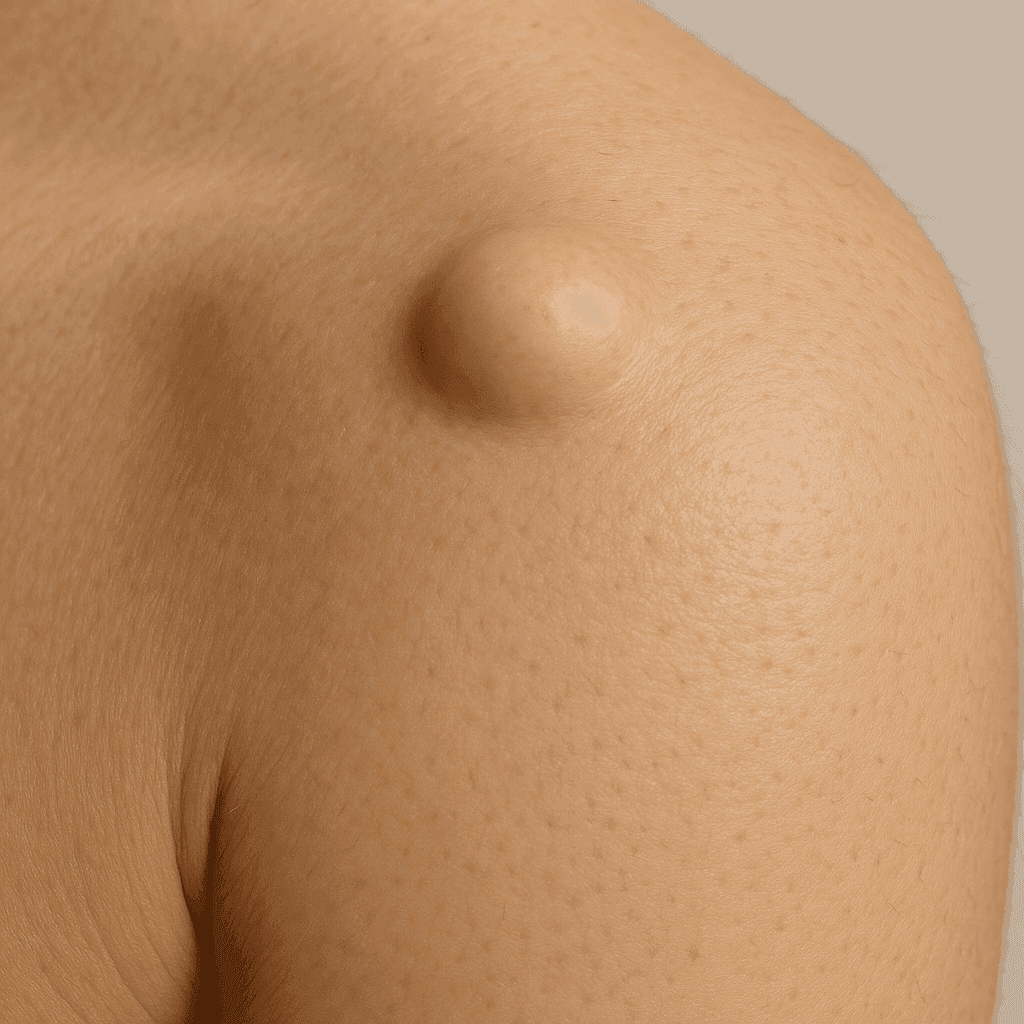
Epidermal cyst
Learn about the symptoms, causes and treatment of epidermoid cyst.
Introduction
An epidermoid cyst, also known as an epidermal or keratin cyst, is a benign skin lesion that results from the accumulation of keratin under the skin. It commonly occurs on the face, neck, back and other parts of the body. Although usually not a serious health risk, it can lead to aesthetic or medical discomfort if it becomes infected or painful.
Symptoms of an epidermoid cyst
Epidermoid cysts often manifest as small, hard nodules under the skin. They can be painless, but sometimes become painful if they become infected. The skin over the cyst may be normal or slightly reddened. In some cases, cysts may have a central opening through which toothpaste-like keratin is secreted.
How do you recognise an epidermoid cyst?
The diagnosis of an epidermoid cyst involves a physical examination by a doctor. In some cases, if the lesion is suspected to be something else, a biopsy may be recommended.
Causes and risk factors
Epidermoid cysts form when keratin, a naturally occurring protein in the skin, accumulates beneath the surface of the skin. They are often the result of a skin injury, such as a cut or infection, which leads to the sebaceous glands closing. Risk factors include acne, skin damage and genetics.
Factors that increase risk
- History of acne or other inflammatory skin conditions
- Genetic predisposition to cyst formation
- Presence of scars from skin trauma
- Weakened immunity
Epidermoid cyst diagnosis
The diagnosis of an epidermoid cyst is usually based on a physical examination. The doctor may opt for a biopsy to rule out other types of skin lesions, such as lipomas or skin tumours. Histopathological examination of the cyst will help confirm the diagnosis by assessing the presence of keratin.
Differences between epidermoid cyst and other lesions
- Lipomas: are soft, mobile and usually painless.
- Skin neoplasms: may have an uneven surface and altered pigmentation.
Treatment of an epidermoid cyst
Treatment of an epidermoid cyst may be necessary if it becomes painful, infected or an aesthetic problem. Most commonly, surgical removal of the cyst is recommended to get rid of the lesion completely. If infected, treatment with antibiotics may be necessary.
Home remedies for cyst management
- Warm compresses: can help relieve pain and aid drainage of the cyst.
- Avoiding pressure: do not squeeze or press the cyst to prevent infection.
- Skin hygiene: wash regularly with gentle cleansers.
Complications and risks
Some epidermoid cysts can lead to complications, such as infections, which may require treatment with antibiotics. In rare cases, the cyst may develop into an abscess. It is important to monitor the changes in the cyst and report to your doctor if you have any new symptoms.
Is an epidermoid cyst dangerous?
Usually epidermoid cysts are not dangerous, but their potential complications may require medical attention.
Epidermoid cyst and other conditions
An epidermoid cyst is often confused with an adipoma, which is a benign tumour of adipose tissue. Unlike lipomas, epidermoid cysts contain keratin and are firmer to the touch.
Association of epidermoid cysts with other skin diseases
These cysts can sometimes co-occur with other skin conditions, such as acne, but are not directly associated with skin cancer.
Epidermoid cyst in different age groups
Epidermoid cysts can affect people of all ages, but are more common in adults. In children, they can be confused with other skin lesions, so it is important that they are assessed by a doctor.
How does an epidermoid cyst manifest in children?
In children, cysts can look like small nodules on the face or neck and are often painless and harmless.
Prevention and prevention
Although epidermoid cysts cannot always be prevented, there are some steps that can help reduce the risk of developing them. It is important to avoid skin damage, use proper skin care and treat any inflammatory conditions, such as acne, that can lead to cyst formation.
Skin care recommendations
- Regular cleansing of the skin with gentle products
- Avoiding aggressive cosmetic treatments
- Consulting a dermatologist if you have problematic skin
Summary
An epidermoid cyst is a common benign skin lesion that can cause discomfort but rarely poses a serious health risk. It is important to monitor cystic changes and consult your doctor if you have any worrying symptoms. Taking good care of your skin and avoiding trauma can help prevent the formation of new cysts.
FAQs
Can an epidermoid cyst disappear on its own?
Epidermoid cysts rarely disappear on their own, but they can shrink and become less noticeable.
Is an epidermoid cyst contagious?
An epidermoid cyst is not contagious. It is formed due to an accumulation of keratin and is not transmitted to other people.
How long does it take to recover from cyst removal?
Recovery time depends on the size and location of the cyst, but usually takes from a few days to a few weeks.