Acne Vulgaris
Learn how to manage acne vulgaris effectively.
Introduction
Acne vulgaris, also known as acne vulgaris, is a common dermatological problem affecting many people worldwide. Effective management of acne requires an understanding of its causes and symptoms. Although most common in teenagers, acne can occur at any age, affecting quality of life and self-esteem.
Understanding acne is key to choosing appropriate treatments and prevention. The aim of this article is to provide a comprehensive approach to the problem, considering both traditional and alternative treatments.
What is acne vulgaris?
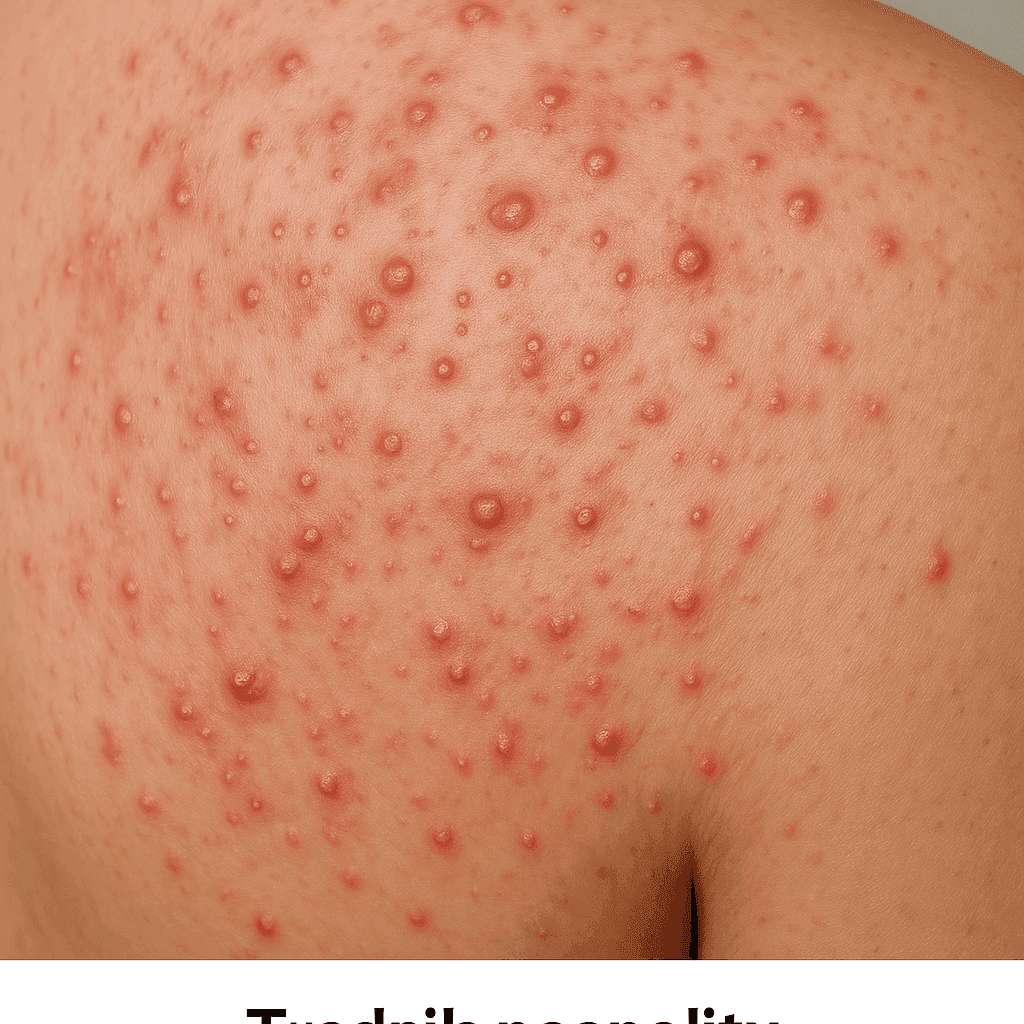
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterised by blackheads, pimples and nodules. It is caused by the clogging of hair follicles by sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
Epidemiology
Acne vulgaris most commonly affects teenagers, but it also occurs in adults. Genetic, hormonal and environmental factors influence its development. It is estimated that around 80% of the population aged 11-30 years experience various forms of acne.
Causes of acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is the result of a complex interaction of many factors. The main causes are:
Genetic factors
Many studies indicate that genetic factors have a significant influence on the development of acne. People who have parents with acne are more likely to develop acne.
The role of hormones
Hormones, particularly androgens, play a key role in the development of acne. An increase in androgen levels leads to an overproduction of sebum, which promotes the clogging of pores.
Impact of diet and lifestyle
Although diet is not a direct cause of acne, there is evidence that certain foods, such as highly processed foods, can exacerbate acne symptoms.
Symptoms of acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris manifests as a variety of skin lesions that may include blackheads, pimples and nodules.
Characteristics of the skin lesions
- Open comedones: black spots, formed by the oxidation of sebum.
- Closed blackheads: white spots that are blocked by the epidermis.
- Pimples: small red bumps with a white centre.
Differences between acne vulgaris and other skin conditions
Acne rosacea, unlike acne vulgaris, is manifested by redness and dilated blood vessels. It is important to diagnose correctly in order to apply the appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of acne vulgaris
The diagnosis of acne is based on clinical assessment, medical history and, if necessary, additional tests.
How do dermatologists diagnose acne?
Dermatologists rely on the appearance of skin lesions and the patient's history. In some cases, they may recommend laboratory tests to rule out other skin diseases.
Importance of medical history and additional tests
A thorough medical history is essential to identify factors that may contribute to the development of acne. Sometimes additional tests such as hormonal tests are required, especially in women with irregular menstrual cycles.
Treatment of acne vulgaris
Treatment of acne vulgaris may involve different strategies, depending on the severity of symptoms.
Pharmacotherapy
Topical and oral acne medications
Topical medications, such as retinoids and salicylic acid, are often the first line of defence. In more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral retinoids or antibiotics.
Antibiotics and their role
Antibiotics, both topical and oral, can be used to reduce inflammation and the number of bacteria on the skin. However, it is important that their use is short-term to avoid bacterial resistance.
Natural treatments
Home remedies for acne vulgaris
Many people turn to home remedies such as honey or aloe vera masks, which can relieve acne symptoms due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Herbal medicine and supplements
Some herbs and supplements, such as tea tree oil and zinc, are popular for their potential benefits in treating acne. However, it is always advisable to consult your doctor about their use.
Dermatological treatments
Dermatological treatments, such as chemical peels and laser therapy, can be effective in treating acne and improving the appearance of the skin. Chemical peels help exfoliate dead skin, while laser therapy works on the deeper layers of the skin to reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of scarring.
Acne skin care
Daily acne skin care is a key part of managing the problem.
Daily skincare routine
Washing your face with a gentle cleanser twice a day helps remove excess sebum and impurities. Avoid products containing alcohol, which can over-dry the skin.
Choosing the right cosmetics
Choose cosmetics labelled "non-comedogenic" that do not clog pores. Products with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can be helpful in controlling acne.
Preventing acne vulgaris
Introducing healthy habits can help prevent acne.
Lifestyle changes
Regular exercise and avoiding stress can help improve the condition of the skin. It is also important to avoid touching your face, which can transmit bacteria.
The importance of diet and hydration
A diet rich in fruit and vegetables and low in simple sugars can support skin health. Remember to keep your body well hydrated, which is key to maintaining skin elasticity and health.
Acne vulgaris and psychological aspects
Acne vulgaris can have a significant impact on mental health and self-esteem.
Impact of acne on self-esteem and mental health
People with acne often experience reduced self-esteem and social anxiety. It is important to take action to support the emotional wellbeing of those affected by acne.
How to deal with the emotional effects of acne?
Talking to a psychologist or attending support groups can help to manage the emotional aspects of acne. It is also a good idea to educate yourself about acne in order to better understand the disease and its impact on your life.
Summary
Acne vulgaris is a common problem that can be effectively managed with the right approach. Understanding the causes and symptoms and choosing appropriate treatments is key.
Remember, it is always worth consulting a dermatologist for professional help and support if symptoms are severe.