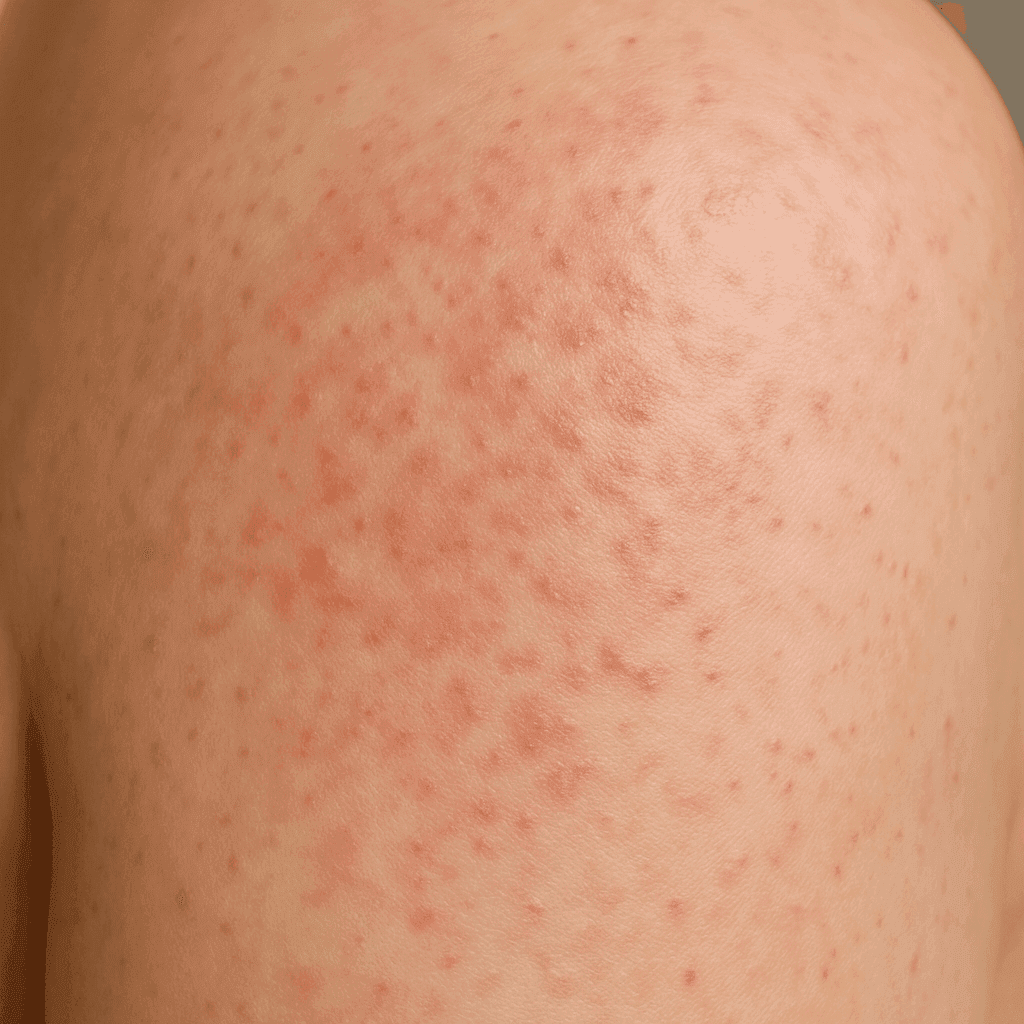
Rosacea
A guide to the causes, symptoms and treatment of rosacea.
What is rosacea?
Definition and background information
Acne rosacea, also known as rosacea, is a chronic skin condition characterised by redness, visible blood vessels and frequent papules and pustules on the face. Although the exact causes of this disease are not fully understood, it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Early diagnosis and treatment can help control symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
Epidemiology and prevalence
Acne rosacea affects millions of people worldwide and its incidence is higher in fair-skinned populations, especially in people over 30 years of age. Women are more likely to develop rosacea than men, but symptoms may be more severe in men. The condition can lead to significant aesthetic and psychological problems, which is why early detection and effective treatment are so important.
Symptoms of rosacea
Early symptoms
In the initial phase, rosacea manifests as redness of the facial skin, which may resemble erythema caused by the sun or emotions. It is often accompanied by a burning or itching sensation. The appearance of dilated blood vessels that become visible on the surface of the skin is also a characteristic symptom.
Advanced symptoms
As the disease progresses, papules and pustules may appear on the skin, resembling juvenile acne. Some patients develop thickening of the skin, especially on the nose, leading to a distortion of the nose, known as rhinophyma. Symptoms can be exacerbated by a variety of factors, such as stress, diet or sun exposure.
Differences in symptoms between men and women
While women are more likely to report problems related to redness and visible capillaries, rosacea symptoms may be more severe in men, especially in terms of skin overgrowth on the nose. Men are also more likely to develop more severe forms of the condition, which may require more aggressive treatment.
Causes and risk factors
Genetics and heredity
Although the exact causes of rosacea are not known, research suggests that genetics play an important role. People whose close relatives suffer from the condition may be at higher risk of developing it. Heredity influences the predisposition to symptoms, meaning that family history is an important risk factor.
Environmental and lifestyle influences
Environmental factors, such as temperature extremes, UV radiation, as well as stress and diet, can influence the severity of rosacea symptoms. It is thought that certain foods and drinks, including alcohol, caffeine and spicy foods, can exacerbate symptoms. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding known triggers can help control the condition.
The role of diet in the development of rosacea
Diet plays an important role in managing rosacea symptoms. Although there are no clear dietary recommendations, patients often notice improvement after eliminating foods that trigger skin reactions. Consideration should be given to eating plenty of fruit and vegetables and avoiding processed foods, which can support skin health.
Diagnosis of rosacea
When to see a dermatologist?
If you notice persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, papules or pustules, it is worth consulting a dermatologist. Early diagnosis can help prevent the progression of the disease and introduce appropriate treatment. A dermatologist can help diagnose rosacea and differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Investigations and diagnostic tests
The diagnosis of rosacea is based mainly on the patient's clinical symptoms and history. The dermatologist may perform a skin examination and recommend additional tests to rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. Sometimes a skin biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Differentiation with other skin diseases
Acne rosacea can be confused with other skin conditions such as teenage acne, eczema or skin allergies. It is crucial to differentiate between these diseases, as each requires a different therapeutic approach. The dermatologist, based on experience and examination findings, is able to make the correct diagnosis.
Treatment of rosacea
Pharmacological treatment
Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs
Antibiotics, such as metronidazole and tetracyclines, are often used in the treatment of rosacea because they help reduce inflammation. These medications can be applied topically in the form of creams or orally, depending on the severity of the symptoms. It is important to use them as prescribed by your doctor to avoid side effects.
Modern therapies and biological drugs
Modern approaches to the treatment of rosacea include biological therapies that target specific inflammatory mechanisms. Although they are available on a limited basis, they may be an option for patients with severe disease who do not respond to standard treatment.
Non-pharmacological treatments
Laser treatments and other dermatological procedures
Laser treatments are an effective method of reducing visible blood vessels and erythema on the facial skin. Procedures such as IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) can help to improve the appearance of the skin and reduce symptoms. It is worth discussing the options available and the expected results with your dermatologist.
Natural methods and home remedies
In addition to drug treatment, many people seek natural methods of dealing with rosacea. Using gentle cosmetics, avoiding irritants and relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation can help manage stress and reduce symptoms.
Skin care for rosacea
Choosing the right cosmetics
Skin care for rosacea requires cosmetics that are gentle and do not contain irritants such as alcohol or fragrances. It is advisable to choose products designed for sensitive skin, which will help to keep the skin barrier moisturised and protected.
Daily skincare routine
Your skincare routine should include gentle cleansing, moisturising and the use of UV filter creams to protect your skin from the sun. Regular use of products with soothing properties can help reduce redness and improve skin condition.
Avoiding factors that exacerbate symptoms
Avoiding factors that can exacerbate rosacea symptoms, such as stress, extreme temperatures, spicy foods and alcohol, is key to managing the condition. Monitoring the skin's reaction to various factors will help identify and eliminate potential triggers.
Preventing rosacea
Lifestyle changes
A healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet and avoiding stress, can help prevent rosacea flare-ups. Awareness and avoidance of triggers, such as UV radiation and poor diet, can minimise the risk of recurrence.
Diet and supplementation
A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins and minerals can support skin health and reduce rosacea symptoms. Supplementation with vitamins C and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, can support skin regeneration and reduce inflammation. However, it is important to consult a nutritionist before introducing supplements.
The importance of sun protection
Sun protection is a key part of rosacea prevention. Using creams with a high UV filter and avoiding direct sun exposure during peak hours can prevent exacerbations of the condition. Wearing a hat and sunglasses also helps to protect the skin.
Rosacea and quality of life
Impact on mental health
Acne rosacea can significantly affect patients' self-esteem and mental health, leading to a reduced quality of life. Stress, uncertainty about appearance and fear of reactions from those around them can lead to depression and social isolation. It is important that patients have access to psychological support and education about the disease.
Coping strategies
Active management of rosacea, including regular visits to the dermatologist, adherence to prescribed therapies and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help to control symptoms and improve quality of life. Support from family and support groups can also be a valuable source of help and motivation.
The latest research and the future of treatment
Innovations in rosacea treatment
The latest rosacea research is focused on identifying new therapeutic targets and developing more effective drugs. Biologic therapies and new forms of topical drugs may significantly improve treatment options for this disease in the future.
Future prospects
Advances in the understanding of the mechanisms underlying rosacea are opening up new perspectives in the treatment of this disease. In the future, more personalised therapies can be expected to be tailored to the individual needs of patients, which may contribute to better symptom control and improved quality of life.
Summary
Key findings
Acne rosacea is a chronic skin condition that requires understanding and appropriate management. Early diagnosis, tailored treatment and lifestyle changes can help control symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. Education about the disease and access to modern therapies are key to successfully managing the condition.
Where to find help and information?
Patients suffering from rosacea should consult a dermatologist to develop a personalised treatment plan. There are many online resources that offer information and support, but it is important to rely on reliable and trusted sources. Health organisations and support groups can also offer valuable guidance and help in managing the condition.